Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Zinc staining
Zinc (or copper) is sometimes used for staining because staining with
these metals represent “negative” staining protocols for SDS-PAGE. The
polyacrylamide in the gel is stained but SDS, which coats the proteins,
is not stained, thus excluding the metal from the protein bands. Zinc
staining is more sensitive than Ponceau but less sensitive than Silver
staining. Importantly, the proteins can be transferred and analyzed after
the staining procedure.
Identification of proteins in gels using
metabolic labeling
Metabolic labeling is a method in which the proteins in cells are la-
beled using radioactive forms of amino acids during their synthesis in
the cell. Metabolic labeling is used to examine the different steady state
pools of proteins within cells. The most common amino acid precursors
are mixtures of methionine and cysteine. Proteins can also
be labeled using precursors that are incorporated into post-translational
modifications, such as phosphate groups or sugars incorporated into
carbohydrates such as the N-linked glycans. The proteins can then be re-
vealed within the gels by exposure to highly sensitive photographic film,
a process known as autoradiography, or by phosphorimaging. Phospho-
rimaging is a technique in which radioactive decay is stored on phosphor
screens, which can then be read by laser imaging into a computer. Phos-
phorimaging is more sensitive and has a greater dynamic range than
film. Phosphorimaging can be used for quantitating
or
but not
tritium
or
Pulse chase analysis
Most metabolic labeling studies use labeling periods of one to a few
hours in an attempt to label the entire pool of a particular protein (or
proteins) being synthesized by a cell. Pulse-chase analysis is a spe-
cialize form of metabolic labeling in which radioactive amino acids are
added for very short periods of time, usually for a few minutes (the
“pulse”), washed away, and then the cells are exposed only to nonra-
dioactive forms of the same amino acids (in excess). The cells are then
harvested and the proteins extracted for study. Pulse-chase analysis is
used to study protein synthesis and processing, to examine the intracel-
lular localization of nascent (newly synthesized) proteins over time, to
examine their secretion, or monitor their degradation.

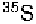
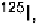


Search WWH ::

Custom Search