Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
constructs that have a particular gene that is fused “in-frame” with the
GFP so that a chimeric protein is expressed. Cells that contain the GFP
can be distinguished from those that do not because of the fluorescent
properties of the protein, making GFP a convenient marker for gene
expression to discriminate transfected from untransfected cells.
E. Other assays using antibodies
Immunohistochemistry (IH or IHC)
Immunohistochemistry is a method that allows for the localization
of antigens in tissue sections using specific antibodies. IH is some-
times referred to as immunocytochemistry (localization of antigens in
cells, rather than tissues) or immunostaining. The reactions between
the antibodies and the antigens in the tissues are most often revealed
by enzymatic reactions (much like western blotting or ELISA) or using
fluorescence, and thus can be visualized under a light or fluorescent mi-
croscope. However, radioactive or colloidal gold-labeled antibodies can
also be used for IH, the latter for EM immunohistochemistry.
The first use of an antibody for IH was reported in 1942 by A. Coons,
who used a fluorescent antibody to reveal antigen distribution in a tissue
section (35). Since then, many improvements in the methods for tissue
harvest and sectioning and the preparation of the tissue for antibody
staining have improved. Most IH is performed using flash-frozen tissue
(using liquid nitrogen, which has a temperature of -196°C, or -320°F)
that is sectioned using cryostats, which allows for preservation of the
original tissue architecture and antigenic structures. IH is an invaluable
tool for studying the basic architecture and cellular localization in tissues,
changes that occur during disease states, and for diagnostic purposes.
Surface plasmon resonance
Surface plasmon resonance is an extremely sensitive method for de-
termining the concentration and affinities of the interactions between an-
tibodies and antigens, or between receptors and their ligands. Surface
plasmon resonance is the response measured when light is reflected
under defined conditions from a conducting film (usually a gold film) that
interfaces two media with different refractive indexes. The sensor sur-
face is coated with a receptor (or antibody). After addition of the ligand,
the response (as resonance units) is measured using very specialized
instrumentation. The RU can be converted concentration of the ligand
on the sensor surface, and the affinities determined. Surface plasmon
resonance is sensitive to changes as little as a
on the sensor.
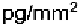
Search WWH ::

Custom Search