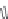Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(A) For the surface charge
(B) For dispersing in polymer matrices
1.
(EtO)
3
Si
SH
2.
(EtO)
3
Si
N
+
1.
(EtO)
3
Si
NH
2
2.
(EtO)
3
Si
(EtO)
3
Si
3.
NH
2
(EtO)
3
Si
3.
N
s
1 or 2
H
(EtO)
3
Si
O
4.
O
O
4.
(EtO)
3
Si
O
n
O
5.
O
5.
Metal,
metal oxide
(Au, Ag,
TiO
2
...)
Quantum
dots
(CdSe, InP, ...)
(EtO)
3
Si
O
P
Na
+
O
(HO)
3
Si
O
O
O
1.
3.
SH
+
NR
NH
2
+
N
R
Organic/
Inorganic
dyes
O
O
R
O
H
S
NR
OH
O
HS-R
SR
S
H
2
N-R
OH
S=C=N
2.
NH
2
+
R
4.
H
H
H
R
O
N
R
(C) For coupling reactions
FIGURE 4.6
Metal and metal oxide nanoparticles and quantum dots (central circles) can be incorporated to make core-
shell structure or homogeneously embedded in silica matrices. Since both have silanol (Si
OH) groups on
the surface, modifications are possible
[43
45]
. (A) Ligands for modifying surface charge: A1 and A3 induce
to positive charge under acidic condition, and its amine is very important in the coupling reaction. A2 also
results in a positive charge independent of pH due to quaternary ammonium salt. A4 “PEGylation” is a good
ligand for bioapplications and it helps to increase circulation time in vivo and to enhance the dispersibility of
nanoparticles in biological buffer and medium reducing the interaction between nanoparticles and proteins.
A5 provides a negative charge and introduces a phosphonate. (B) Ligands for modifying dispersion in
polymer matrices: B1 is widely used in dentistry to mix bis-GMA/TEGDMA resin. Nanoparticles having
terminal double bonds via condensation of B2 can be polymerized with monomers such as styrene. Because
most polymers such as polystyrene and polyethylene are hydrophobic, B3-modifed nanoparticles can be
readily blended into common polymers. The B4-modifed materials can make epoxy resin composites, and the
B5-modified structures can form PMMA, poly(methyl methacrylate) composites, a major component of
contact lenses. (C) Ligands for coupling reactions: the surface reaction of nanoparticles is different from a
general reaction due to possible hindrance of spatial configuration and therefore a highly effective coupling
reaction might be required. C1 is the formation of thioether. Nanoparticles condensed with B1 are reacted
with maleimide-linked protein or antibody. The amine terminated can be synthesized with A1 and A3. As
most biomolecules including proteins have an amine group, C2 reaction is very useful for tagging proteins or
used on the surface of MSNs with isothiocyanated dyes such as RITC (rhodamine B isothiocyanate) and FITC
(fluorescein isothiocyanate). C3 is frequently used in biotinylation reacted with a primary amine and the
activated biotin by N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) with a linker. The epoxide-terminated B4 can be used not