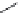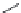Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
composite (RBC) materials, clinical longevity of dental amalgam remains superior
[49]
. Dental
composite resins have been used as popular materials to restore teeth since their introduction about
50 years ago
[50]
. Compared to dental amalgams, they have less safety concern and possess better
esthetic property. Based on the report in 2005, the composites were used in more than 95% of all
anterior tooth direct restorations and about 50% of all posterior tooth direct restorations
[51]
.
Dental composites are increasingly popular due to their esthetics, direct-filling ability, and
enhanced performance. Dental composites are typically composed of four major components:
organic polymer matrix (2,2-bis[p-(2
0
-hydroxy-3
0
methacryloxypropoxy)phenylene]propane
(BisGMA), bisphenol A ethoxylated dimethacrylate (BisEMA), triethylene glycol dimethacrylate
(TEGDMA), urethane dimethacrylate (UDMA), etc.)
(
Figure 2.3
),
inorganic filler particles,
O
O
H
2
H
2
H
2
H
2
CH
3
C
CH
2
H
2
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
CH
CH
O
C
O
O
C
O
CH
3
OH
OH
CH
3
CH
3
BisGMA
O
CH
3
O
H
2
H
2
H
2
C
C
O
C
O
C
C
C
CH
2
C
C
O
C
C
O
H
2
CH
3
H
2
2
2
CH
3
CH
3
BisEMA
O
O
H
2
CH
3
H
2
H
2
H
N
N
O
C
CH
2
H
2
C
C
H
2
C
C
O
C
C
CH
C
C
O
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
O
H
2
H
2
H
2
H
2
CH
3
O
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
O
UDMA
CH
3
O
C
H
2
H
2
H
2
H
2
C
C
O
C
C
C
O
C
C
C
O
C
O
CH
2
C
H
2
H
2
H
2
CH
3
O
TEGDMA
FIGURE 2.3
Chemical structures of monomers used in dental nanocomposites.