Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1000
1
0
c
e
3
−
1000
2
−
2000
d
−
3000
20
60
100
140
180
220
260
Scratch distance (
µ
m)
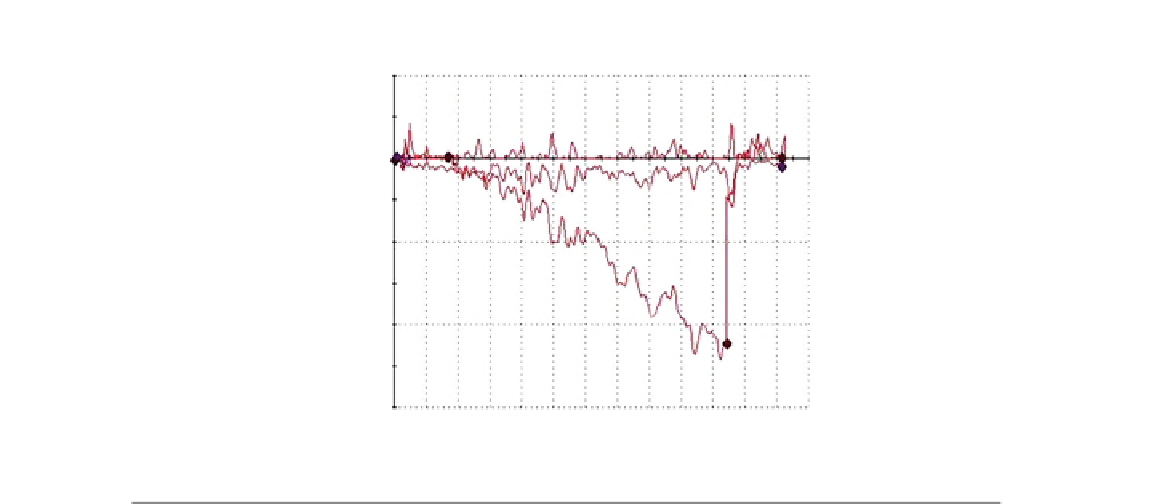
FIGURE 13.9
Scratch test performed using the nanoindenter showing an almost complete recovery of the Co
IF-coated
file after release of the load. (1) Surface profile of the pristine surface, (2) scratch test with increasing force,
up to 30 mN, and (3) surface profiling after the pressure release.
1
fully duplicated in the laboratory. Nevertheless, these experiments were conducted in various best-
fit models.
The following sections describe various experimental friction models used to evaluate the effect
of IF coatings of orthodontic wires on the friction force.
13.4.4.1
SS wires with IF-WS
2
NP impregnated in electroless Ni
P film
In the first set of experiments, a system which simulated the sliding of a tooth along an archwire,
described previously by Redlich et al.
[40]
was utilized. Upper incisor SS brackets were bonded to
aluminum plates by a bracket-mounting apparatus. This apparatus ensured the accurate and similar
positioning of the brackets on the plates. The plates were then connected to the base of a universal
mechanical testing apparatus (Instron 4502) through a device with three different notches angulated
at 0
,5
, and 10
to the long axis of the device (
Figure 13.10
). Angulations represent the contact
angle between the wire and bracket during the movement of the tooth.
In this setup, the tensile tester was set to move the bracket down along the wire at a constant
speed of 10 mm/min to a distance of 5 mm. The test begins with a steady increase in the force and
reaches a maximum when movement begins on the wire. This maximum force represents the static
friction and it is the force that is of interest in this case. A run-in period was needed before testing
the coated wires with Instron. The run-in was carried out by repeated back and forth movements of
the wire in a bracket slot before connecting the wire to the Instron. A new bracket was used for
each testing. The highest angle was tested in the dry and wet mode. Deionized water was used to
simulate the wet conditions in the mouth.
Table 13.1
summarizes the results of the mechanical