Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
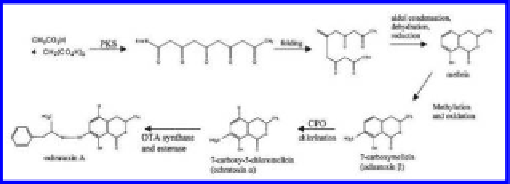
Figure 3.
Biosynthetic pathway for ochratoxin A. PKS Polyketide synthase; CPO.
Chloroperoxidase (Moss 1998).
Tricothecenes
Trichothecenes are a group of mycotoxins which are produced by a variety
of different
Fusarium
species. However a number of other fungal genera
are also known to produce trichothecenes. Trichothecenes are known to
be produced by at least 24 different species (Marasas et al. 1984).
Fusarium
spp., produce the widest variety of different trichothecene compounds
among which the type B-trichothecenes deoxynivalenol (DON) and
nivalenol (NIV) as well as the type A-trichothecenes T-2 toxin, HT-2 toxin,
Neosolaniol (NEOS) and Diacetoxyscirpenol (DAS) are the most common
and/or toxic compounds isolated from natural sources. The four important
trichothecene producers are
F
.
equiseti
,
F
.
graminearum
,
F
.
moniliforme
and
F
.
sporotrichioides.
Because of the large numbers of trichothecenes
produced by
Fusarium
spp., together with the fact that they are produced
in mixtures even under pure culture conditions. It is often diffi cult to
identify the causative toxins, even though the infecting fungal species
is known. However trichothecenes are known to cause alimentary toxic
aleukia, fusariotoxicoses and to be cytotoxic to mammalian cells. They
are immunotoxic and potent inhibitors of protein synthesis, which can
predispose animals to other diseases and mask the underlying toxicoses
(Prelusky et al. 1994). Dietary exposure to trichothecenes can lead to an
increased susceptibility to other microbial infections (Pestka and Bondy
1994). Pigs and other monogastric animals including humans appear to
display the greatest susceptibility to these toxins.
The trichothecene biosynthetic pathway has been well characterized
in a number of species, most notably
F. graminearum
and
F. sporotrichioides
(Brown et al. 2001, Kimura et al. 2003). Sequence from the trichothecene
gene cluster, specifi cally the
tri4, tri5
and
tri6
genes, has been exploited
in the development of generic PCR-based assays for the detection of
trichothecene producers, as these genes are present in all trichothecene-
producing
Fusarium
species. The
tri6
gene is a transcriptional activator that
can regulate expression of both
tri4
and
tri5
. Primers specifi c to
tri6
gene