Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
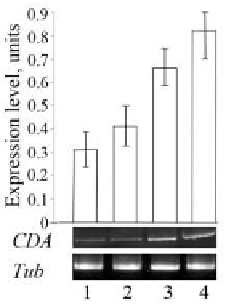
Figure 5.
Expression level of
CDA
gene
in leaves of wheat were infected with septoria glume
blotch pathogenic agent of
S. nodorum
strains 4VD (1), 6VD (2), 9MN (3), Bas1 (4) (10 hr
after infection)
.
Expression of CDA gene was normalized against expression of TUB gene/
The signifi cance of differences between strains
was determined with a t-test and indicates
a difference signifi cant at the P<0.01 level
.
CDA
activity allow us to draw a conclusion about the importance of this
enzyme in the infectious process of pathogens. Data obtained in this
study suggest that PCR-diagnostics is effective not only in identifying
the presence of the pathogenic fungus in plant tissues (Fraaije et al. 1999,
2002, Ryazantsev et al, 2009), but also in determining their degree of
aggressiveness. Effective control of wheat seed infection by the fungus
S. nodorum
, using modern molecular genetic techniques, which include
PCR, allows to forecast epiphytoties of Septoria glume blotch and to take
measures to eliminate them.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work was fi nanced from the state contract P339 the Ministry of
Education and Science of the Russian Federation.
References
Abramova, S.L., D.Yu. Ryazantsev and T.M. Voinova et al. 2008. Diagnosis of
pathogenic fungi
Septoria tritici
and
Stagonospora nodorum
using FLASH-PCR.
Bioorganic Chemistry
.
34:
107-113.
Atkins, S.D. and I.M. Clark. 2004. Fungal molecular diagnostics: A mini review.
J. Appl. Genet
.
45:
3-15.
Beck, J.J. and J.M. Ligon. 1995. Polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection
of
Stagonospora nodorum
and
Septoria tritici
in wheat.
Phytopathology.
85:
319-324.