Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Carbohydrases
In most food applications, wherein carbohydrate hydrolyzing enzymes
are applied, the substrate is derived of plant material. In plants,
the carbohydrates can be subdivided into starch and non-starch
polysaccharides. The latter class consists of cellulose, hemicellulose, which
is made up of xylans, mannans, non-cellulosic β-glucans, of which the
composition can vary with specifi c plant species and pectins. For each
type of carbohydrate specifi c fungal enzymes are produced and applied
in food processing.
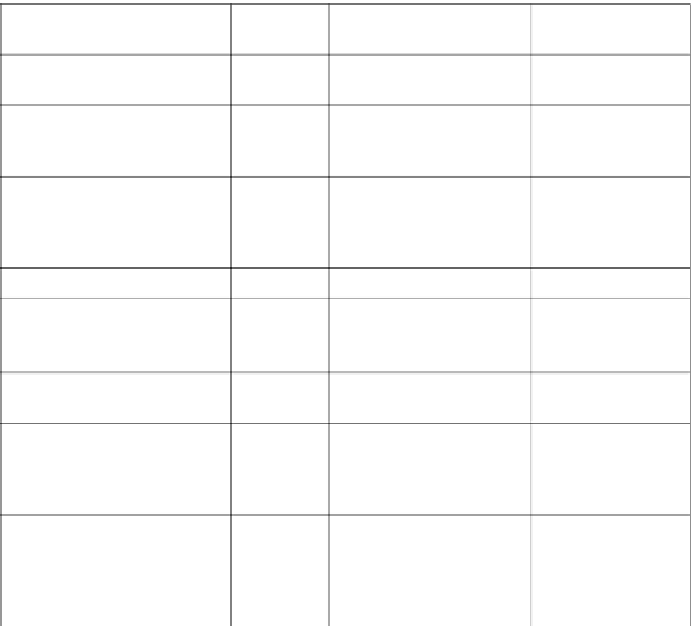
Table 1.
Major fungal carbohydrases in food applications.
Enzyme type
EC
number
Organism of origin
Applications
3.2.1.1
Aspergillus oryzae
bread, beer,
alcohol, fruit juice
α-amylase
amyloglucosidase
3.2.1.3
Aspergillus niger
bread, beer,
alcohol, sugar
syrup
3.2.1.8
Aspergillus niger,
Trichoderma reesei,
Humicola insolens,
Thermomyces lanuginosus
bread,
biscuits, beer,
oligosaccharides
β-xylanase
arabinofuranosidase
3.2.1.55
Aspergillus niger
Bread
3.2.1.4/
3.2.1.99/
3.2.1.21
Trichoderma reesei,
Talaromyces emersonii
bread, beer
Cellulase(β-glucanase/
cellobiohydrolase/
β-glucosidase)
3.2.1.78
Aspergillus
sp.,
Trichoderma
sp.
coffee,
oligosaccharides
β-mannanase
Aspergillus niger,
Aspergillus aculeatus
Pectinase(polygalacturonase,
pectin lyase, pectate lyase,
pectin methyl esterase)
3.2.1.15/
4.2.2.10/
4.2.2.2/
3.1.1.11
fruit & vegetable
processing, wine
Aspergillus oryzae,
Aspergillus niger
3.2.1.23
milk, yoghurt,
dietary
supplement,
whey processing,
oligosaccharides
β-galactosidase (lactase)
Amylases
Starch, the major storage carbohydrate in wheat, rice, maize and potato, is
most commonly used in human nutrition around the world. The glucose
units of starch are linked by α-(1,4)-glycosidic linkages, with only a