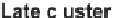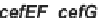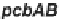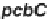Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 2.
Gene organization of the cephalosporin gene clusters in A. chrysogenum.
The “early” cluster includes the biosynthetic (
pcbAB, pcbC, cefD
1 and
cefD
2) and the
transporter genes (
cefT, cefM
and
cefP
) for penicillin N biosynthesis. The late cluster
includes
cefEF
and
cefG
genes for cephalosporin C biosynthesis (conversion of penicillin
N to cephalosporin C).
four introns and encodes a 71-kDa protein with similarity to fatty acid acyl-
CoA synthetases. The second gene,
cefD2
, contains one intron and encodes
a protein homologous to a-methyl-CoA racemases of eukaryotic origin.
Disruption of either of these genes results in a loss of IPN epimerase activity,
lack of cephalosporin C production and accumulation of the intermediate
IPN in the culture broth (Ullán et al. 2002b).
Downstream of the
pcbAB
gene there is an open reading frame
named ORF3 that encodes a D-hydroxyacid dehydrogenase (forming
the corresponding α-keto acid) (Fig. 2). Targeted inactivation of ORF3 by
deletion of ORF3 and ORF7 genes and reintroduction of ORF7 showed that
it does not play an essential role for cephalosporin biosynthesis, probably its
function may be replaced by other redundant hydroxyacid dehydrogenases
(Ullán et al. 2002a).
Early Cluster: Genes Involved in Traffi c and Secretion
of Cephalosporin Intermediates
In addition, the “early” cluster of genes for β-lactam biosynthesis contains
three genes
cefT
(ORF7) (Ullán et al. 2002a),
cefM
(Teijeira et al. 2009) and
cefP
(Ullán et al. 2010) encoding proteins involved in the traffi c of β-lactam
intermediates in
A. chrysogenum
.
Located downstream of
pcbAB
and in the opposite orientation there is
a gene named
cefT
that encodes a protein containing 12-transmembrane
spanning domains (TMSs) with the characteristic motifs of Drug:H+
antiporters of the 12-TMS class. Targeted inactivation of
cefT
does not