Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
of these assays are based on FRET. In the case of hybridization assays,
the length of the sequence needs to be small enough to position
the donors and acceptors within the Förster distance in order to
achieve eficient FRET eficiencies, leading to great sensitivity.
93,94
This limitation may be overcome by conducting the assays on metal
surfaces. Since the transfer distance can be increased 10-fold by a
metal particle, the FRET assays can be performed if the donors and
acceptors are 150 base pairs apart rather than the more typical 15
base pair difference. Alternatively, metal-enhanced FRET may be
used to probe longer range structures in DNA, RNA, and ribosomes.
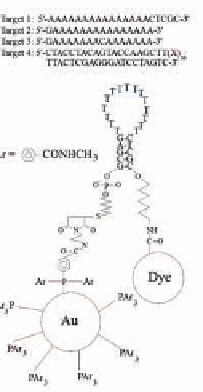
Figure 10.10
(A) Schematic drawings of the two conformations of the
dye-oligonucleotide-Au conjugate and of the Au-quenched
molecular beacon. (B) The oligonucleotide has a chain
of 15 thymidines embedded into two complementary 5-
nucleotide-long segments. The two hybridized segments
form a hairpin stem with the probe sequence located in the
hairpin loop. The maleimide of a monofunctional Au cluster
that is 1.4 nm in diameter and passivated with on average
12 phosphine ligands is covalently linked to the 5
′
-terminal
phosphate through a (CH
2
)
6
-SH group. The dye is linked to
the 3
′
-hydroxyl group by a (CH
2
)
7
-NH
2
linker. Reprinted
with permission from Ref. 96.
Molecular beacons (MBs) are commonly used for the detection
of nucleic acids.
95
Generally, MBs are DNA sequences composed
of one target-recognition region of about 15-30 bases lanked by



Search WWH ::

Custom Search