Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
of
Escherichia coli
(
E. coli
). Type 1 imbriae present on the surface
of Enterobacteriaceae, such as
E. coli
, are responsible for their
mannose- and mannoside-binding activities. Thus, incubation of
E. coli
with the biofunctional Man-Au NPs yielded brightly
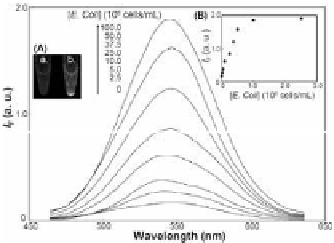
luorescent cell NCs. The relationship between the luminescence
signal and the
E. coli
concentration is linear over the range from
1.00 × 10
6
to 5.00 × 10
7
cells/mL (
R
2
= 0.96), with the LOD of
E. coli
being 7.20 × 10
5
cells/mL (Fig. 9.11). In contrast to standard methods
for pathogen detection, which require up to 2 days for analysis, the use
of these luminescent carbohydrate-functionalized Au NDs allows the
presence of
E. coli
to be detected within as little as 3 h.
Figure 9.11
Luminescence spectra of Man-Au NPs (25 nM) used as
probes for the detection of
E
.
coli
(from 2.50 × 10
6
to 1.00
× 10
8
cells/mL). Inset (A): Visualization of Man-Au NPs (25
nM) in the (a) absence and (b) presence of
E
.
coli
(2.50 ×
10
8
cells/mL) upon excitation (365 nm) under a hand-held
UV lamp. Inset (B): Plot of luminescence intensity (545 nm)
versus
E
.
coli
concentration. Reprinted with permission
from Ref. 25.
9.6 Conclusion
Research on luminescent Au NCs and luminescent Au NPs is
attracting increasing interest. Great progress has been made in
understanding the fundamental size- and surface-dependence
of the optical properties of these Au nanomaterials, as well as in
developing sensitive and selective sensors from them. Nevertheless,
much work remains to be done to better understand and manipulate
their properties. For example, the luminescence properties of
luminescent Au NPs are different from those of Au NCs, but remain
















Search WWH ::

Custom Search