Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
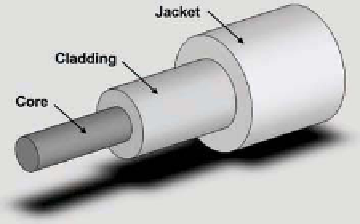
a cylindrical optical waveguide along its axis to radial, and
can generally be divided by its refractive index into 3 layers:
core, cladding, and the outside protection jacket. The core and
cladding of the optical iber transmit the basic elements of light.
Fiber optic sensors are not affected by electromagnetic noise
or magnetic interference. The impact of ionizing radiation can
also be avoided though the use of radiation treatment making it
suitable for demanding environments, such as nuclear power
plants. Also, since the iber optic sensors use the same iber as
both a sensor and signal transmission line, they can be placed in
areas that traditional sensors with wires could not, such as small
or not easily accessible locations. Fiber optic sensors use light as
the transmission medium rather than current or voltage, so there
is no risk of electric shock, making them suitable for medical
measurements. Fiber optic materials do not corrode, and are thus
suitable for deep-sea engineering and environments where there
is risk of chemical corrosion. Glass iber has a higher temperature
resistance gauge than metal, and longer-term stability and
fatigue resistance, making it suitable for long-term monitoring.
Since optical ibers have been used in long distance optical iber
communications, iber optic sensor technique is easily adapted to
long-distance telemetry. In addition, the use of wavelength division
multiplexing technique in optical communications also helped the
same optical ibers with multi-point measurement, which has lead
the iber optic sensors being widely used in aerospace, medicine,
chemistry, earth engineering, civil engineering, and other ields as
well.
Figure 6.15
Structure of an optical iber.
Fiber optic sensors rely on the measurement of physical
(chemical) content, hence, inding a mechanism to modulate the

Search WWH ::

Custom Search