Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
6.3.3 HolographicExposure
Holographic exposure uses the interference fringe pattern,
consisting of a set of equally spaced bright and dark lines, of two
intersected laser beans to expose the photoresist coated on a
substrate. The exposed photoresist is then chemically developed
to form a pattern of straight groves with a sinusoidal proile. The
developed photoresist with a pattern of straight groves can be used
as a master grating for replication, or as a mask for anisotropic
etching of the substrate. Due to the fact that optical masks are not
required in the fabrication processes, holographic exposure is also
considered one of the maskless lithography techniques. It is suitable
for fabricating gratings with high grove densities and large areas, and
is widely used in the fabrication of commercial gratings and actively
researched [23-28]. Holographic gratings, however, cannot be easily
blazed because of their sinusoidal grove proile, and their eficiency
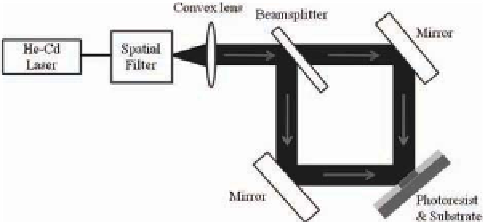
is usually considerably less than a comparable ruled grating. Figure
6.10 shows the schematic diagram of the experimental facility
Figure 6.10
Schematic diagram of the experimental facility used for
holographic exposure.
Figure 6.11
SEM image of a holographic grating with a grove density of
1800 groves/mm.


Search WWH ::

Custom Search