Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
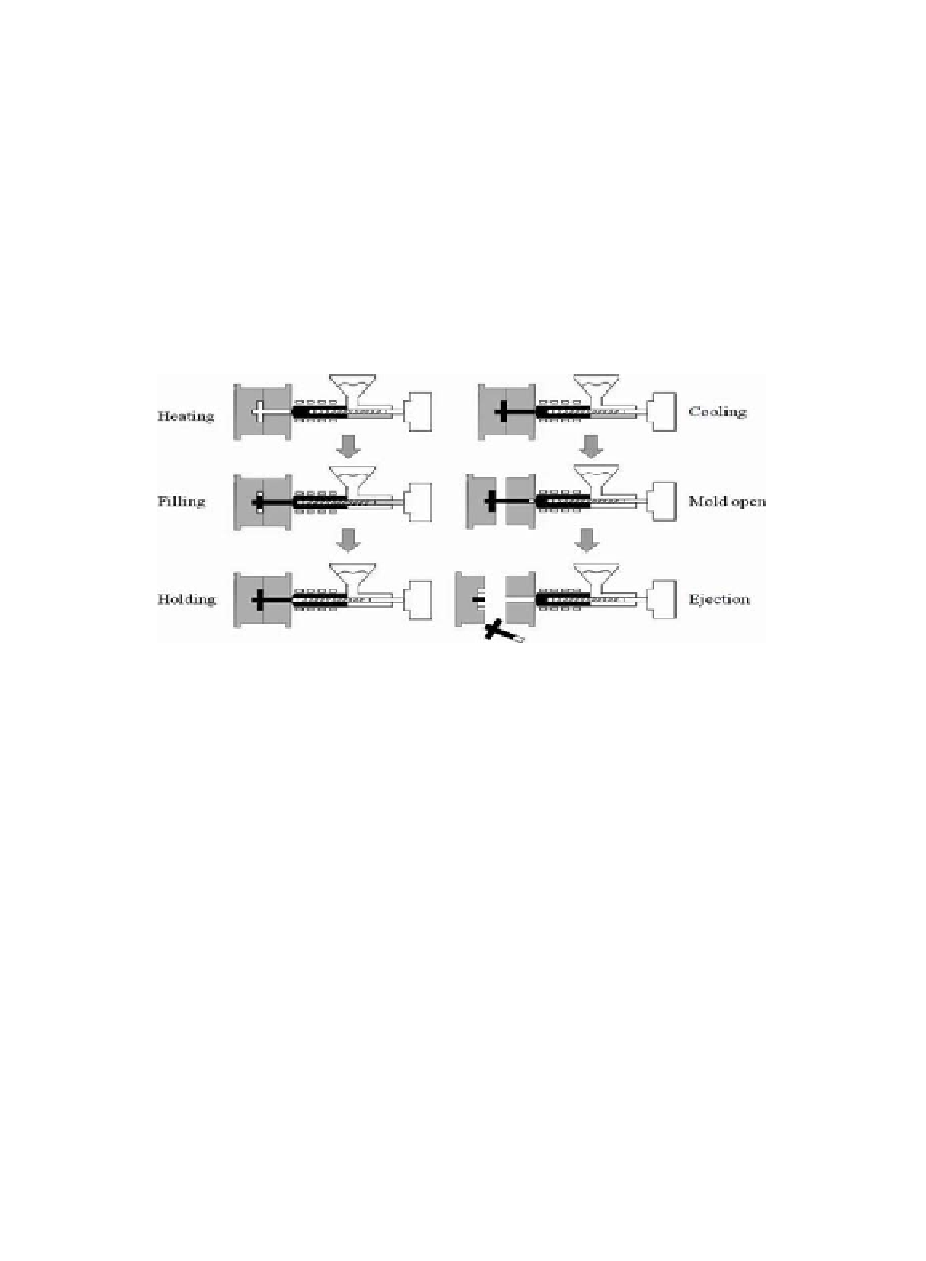
Micro-injection molding makes extensive use of thermoplastics,
but thermosetting plastics or ceramic materials are also used. The
main process of injection molding requires putting plastic granules
in a heating tube and heating them until they reach a liquid state.
Then a nozzle is used for high-pressure, high-speed injection of the
material, which passes through the sprue and runner to the mold to
be completed under pressure in the cavity. After cooling, the molded
object is released via the ejection system. The process includes
illing, packing, cooling, and other steps (as shown in Fig. 6.6). The
micro-injection molding technique provides the major advantage
of being able to produce reined, complex shapes in small-sized
inished products.
Figure 6.6
Micro-injection lowchart.
6.2.4
Bonding
The biosensor chip bonding technique is part of the manufacturing
process, but it can affect the overall accuracy of the most critical
aspect: a good and easy-to-operate interface. As such, the kind of
interface between the plastic polymers to construct the biosensor
chip by a bonding technique can be used as a basis for classiication.
It can be divided into two categories: attachable medium and non-
attachable medium. Bonding methods for the attachable medium
include the organic bonding medium, UV sensitive curable bonding
medium, or double-sided tape style. The non-attachable medium
uses fusion bonding for bonding. These bonding techniques can be
characterized as follows.
Attachable medium mounting/bonding technique: Bond
two plastic joints with organic dielectric [10] using appropriate

Search WWH ::

Custom Search