Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
As shown in Fig. 5.6, real-time detection of biomolecular
interaction of anti-DNP with DNP on the GNP surface shows a response
time of 300 s. As suggested by Eq. 5.25, reduced channel height will
lead to shorter response time. For this sensing coniguration, the
height of the microluidic channel can be easily adjusted. Thus, the
integration of a PW-PPR biosensor and a microluidic chip can be
easily optimized.
5.5
Tubular Waveguide-Based PPR Biosensor
A tubular waveguide (TW) can be a light guiding tube or a light
guiding capillary. Tubular waveguide sensors typically have a
chemically sensitive inner coating in the TW. They are multifunctional
devices in being optical waveguides, sample cavities of deined
volumes, sampling devices, low-through cells, mechanical support
for sensor coatings, and wavelength discriminators.
87
As a device
for direct sampling, samples may be drawn by capillary action, and
this is considered to be particularly convenient in the case of blood
and other biological luids. In addition, TWs may be fabricated by
simple and inexpensive means and therefore are ideally suited for
disposable sensors.
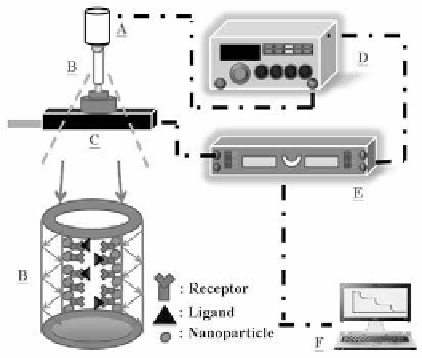
Figure 5.7
Schematic representation of the experimental setup for the TW-
PPR biosensor to make measurements: A, light emitting diode;
B, gold nanoparticles-modiied glass tube; C, photodiode; D,
function generator; E, lock-in ampliier; F, computer.
















Search WWH ::

Custom Search