Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
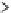
FIGURE 5.7
The velocity profile of blood flow-
ing through a cylindrical vessel using the Casson
model. The profile is blunter than a purely
Newtonian fluid's velocity profile because the
fluid that is between the centerline and
r
y
flows as
a solid. At
r
y
, the shear stress surpasses the yield
stress of the fluid (
R
r
y
τ
y
) and the viscous forces take
effect.
and therefore, the Casson model can be rewritten as
2
r
p
p
r
2
dp
dx
p
τ
γ
ð
5
:
2
Þ
5
1
y
Solving this for shear rate we get
!
2
r
2
du
dr
5
γ
5
1
η
r
2
dp
dx
p
τ
y
ð
5
:
3
Þ
2
2
If we integrate this function from
r
y
to
R
(tube radius), over the appropriate reduced
cross-sectional area, we get the following function for the velocity profile, keeping in mind
that the velocity is constant between the centerline (
r
0) and
r
y
:
5
8
<
0
@
1
A
1
4
dp
dx
8
3
r
0
:
5
R
2
r
2
R
1
:
5
r
1
:
5
ð
Þ
1
2
r
y
ð
R
r
Þ
r
y
r
R
2
2
2
2
2
#
#
y
η
0
1
u
ð
r
Þ
5
ð
5
:
4
Þ
:
3
p
R
p
1
4
dp
dx
p
r
y
1
3
p
r
y
@
A
r
r
y
2
2
1
#
η
The Casson model is a very useful representation of blood flow through the arterial sys-
tem, but it tends to complicate the computations by hand. The following sections discuss a
method to simplify the calculations, but these methods may not accurately represent the
blood flow conditions.
Because plasma behaves as a Newtonian fluid, the non-Newtonian fluid properties are
more than likely attributed to the cellular component of blood. Red blood cells, the major-
ity of the cellular component, in the fluid phase can form aggregates termed rouleaux
(
Figure 5.8
). Interestingly, the presence of rouleaux in the blood is dependent on the shear
rate at which the fluid is flowing. At lower shear rates, rouleaux are more prevalent, likely
due to the greater time that cells can come into contact with each other and/or proteins in
the blood. It has been speculated that as the shear rate approaches zero, blood will act as a
viscoelastic solid, because all of the red blood cells will form into one large aggregate. As






































Search WWH ::

Custom Search