Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
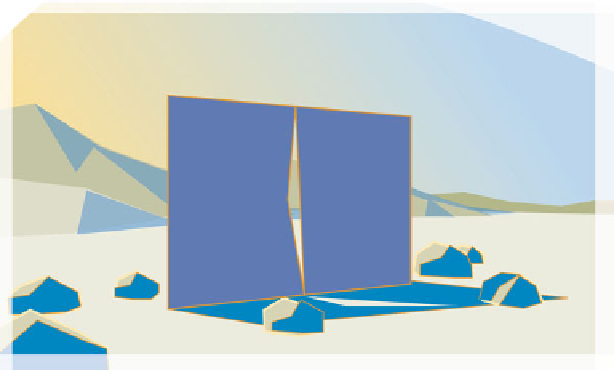
Fig. 9.7
A gap between two polygons. It is possible that the three vertices on the right edge of the
left polygon could be placed in a straight line. This would hide the gap without removing it
9.3
Technical
9.3.1
Introduction
Technical errors can cause application crashes and render errors, from minor to
serious. Most of the errors in this section are considered to be extremely serious and
should not be found in any model. If they are present, the model is not fi t for use in
a professional context.
9.3.2
Aspect Ratio
In Sect.
6.5.3
you were shown how to calculate the aspect ratio for an image. Aspect
ratio is also relevant to 3D models and the faces they are made of. The aspect ratio
of a polygon is calculated in the same way as for an image. There are two reasons
why the aspect ratio of a polygon is of interest to modelers. The fi rst is that the
aspect ratio is another way to measure parts of the object. If the aspect ratio doesn't
match the target, then the likeness suffers. As a technical error, if the aspect ratio is
too large or too small, the polygon will be so narrow that some renderers will have
problems rendering them in the right position relative to other polygons. This is
known as a
polysorting error.
A polysorting error is when the renderer cannot decide whether a polygon is in
front of or behind another polygon. This is not a problem with off-line renderers
such as those used in the fi lm industry, but real-time renderers used in video games
Search WWH ::

Custom Search