Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
assay can be used to eliminate false positive results generated from PCR
amplification.
For viral detection, MBs hold great promise as a method for viral gene
detection in living host cells.
90
However, the inability to grow many of the
enterovirues (
Norwalk
,
Adenovirus
,
Astrovirus
, etc.) in culture limits the utility
of the method for testing environmental samples.
8.2.3.8. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) is a phenomenon in
which energy is transferred from an excited fluorophore, the donor,
to a light-absorbing molecule, the acceptor. Like MBs, it uses fluoro-
phores and quenchers; however, it is designed to use two primers that
bind to their target so that the distance between the donor dye on one
primer is in close proximity to the acceptor dye on the other primer
(within 10nm) to cause a fluorescent reaction that can be detected
(
Fig. 8.12
). The extreme sensitivity of the efficiency of the energy transfer
from donor to acceptor has proven to be a valuable means for studying
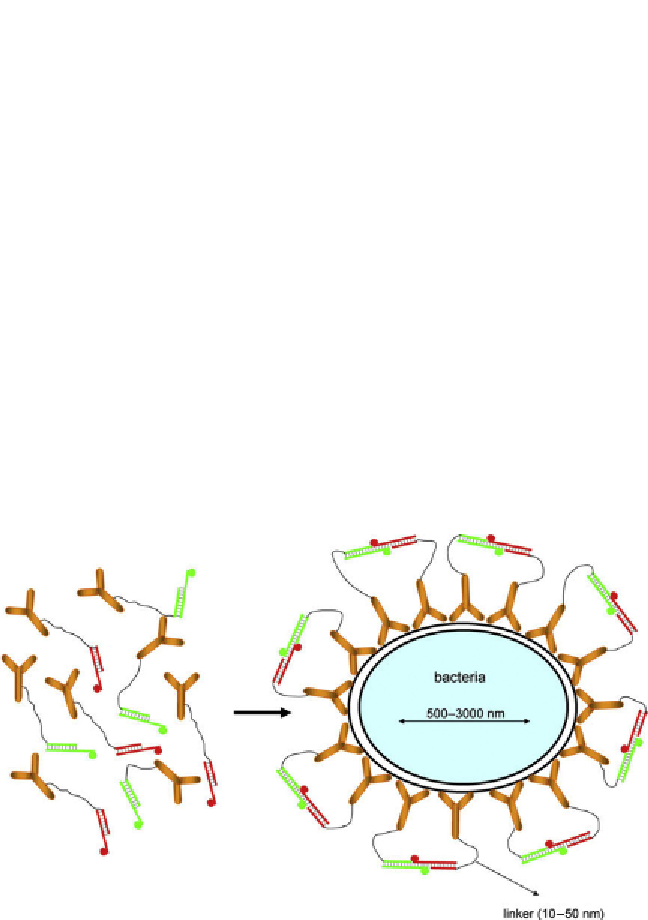
Figure 8.12
Illustration of the FRET system. A pair of antibodies (or other specific bind-
ers) recognizing overlapping target sites can be labeled with fluorophores, which can
function as donors and acceptor in FRET. In the presence of the target, both antibodies
(binders) will bind to the target, bringing their respective fluorophores close enough
together that it will result in FRET, which can be used as signal for target detection.
Source:
Adapted from Ref.
97
.
(For color version of this figure, the reader is referred to the
online version of this topic.)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search