Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
bacterial species present in the ballast water within 9h.
77
Conventional
RT-PCR was found to be more sensitive with the detection of 1 cfu mL
−1
in 7 h, presumably because DNA not RNA was the target molecule.
NASBA has also been successfully developed for the detection of a
number of RNA viruses from food and water.
78,79
The advantages of this
method are the low detection limits, rapid assay times, and in some cases
with stringent controls, quantifiable results. Because many viruses are hard
to culture, the use of molecular methods such as NASBA can provide infor-
mation about the presence and infectivity of the virus.
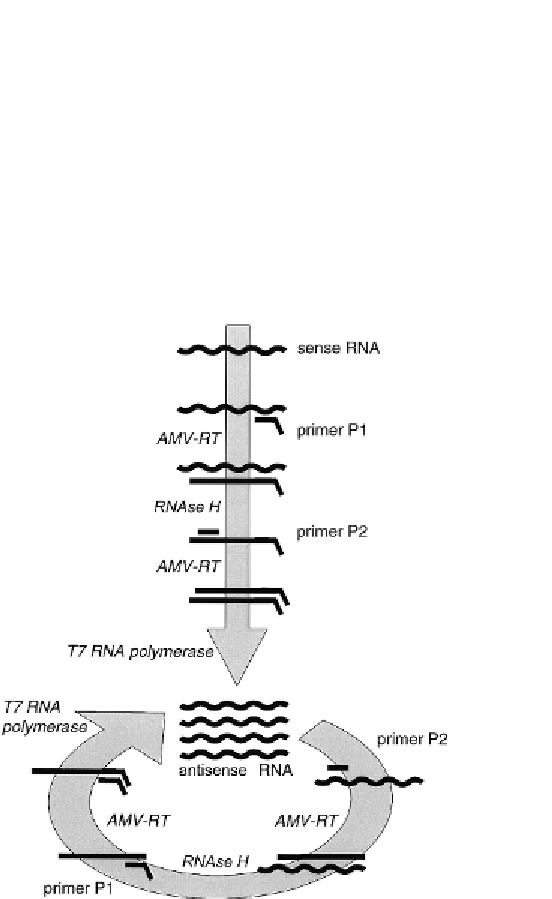
Figure 8.8
Nucleic acid sequence based amplification (NASBA) is used to amplify RNA
sequences. RNA template is given to the reaction mixture, the first primer attaches to
its complementary site at the 3
′
end of the template. Reverse transcriptase synthesizes
the opposite, complementary DNA strand. RNAse H destroys the RNA template the sec-
ond primer attaches to the 5
′
end of the DNA strand. T7 RNA polymerase produces a
complementary RNA strand which can be used again, so this reaction is cyclic. Source:
Search WWH ::

Custom Search