Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
tolerance to high temperatures,
36
is label-free, and is relatively inexpen-
sive.
35
QCM devices typically operate at frequencies between 1 and 10 MHz,
and the entire piezoelectric substrate is used for wave propagation. In con-
trast, surface acoustic wave (SAW) sensors operate at higher frequencies
(50 MHz to low GHz), and the acoustic energy is confined to a thin surface
layer on the substrate. As the Sauerbrey equation shows, the sensitivity of
this type of sensor is proportional to the square of the frequency. Therefore,
the principal advantage of SAW over QCM is higher sensitivity.
Piezoelectric-excited millimeter-sized cantilever (PEMC) sensors have
been applied for the detection of several toxins, proteins such as rabbit
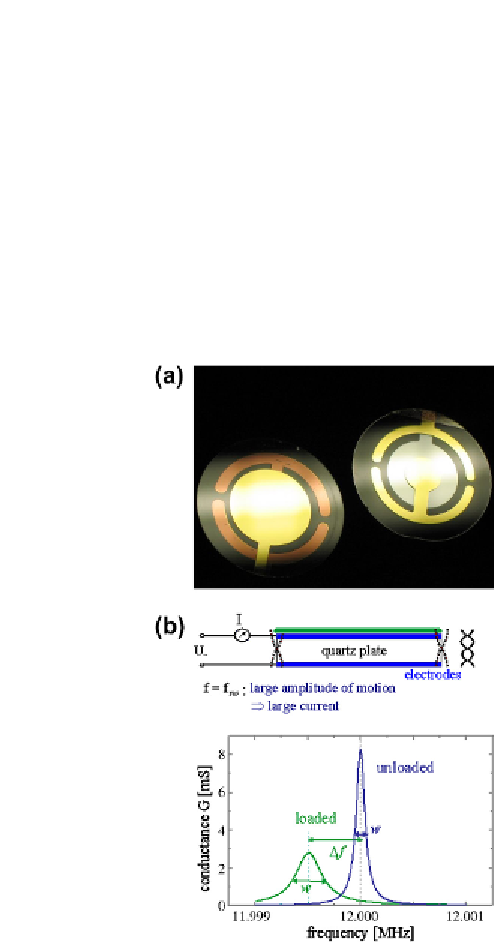
Figure 7.7
QCM schematic. (a) Image of a typical QCM electrode/sensing area.
(b) Schematic of operation showing the shear movement. Wikicommons Source:
gif?uselang=en-gb
(For color version of this figure, the reader is referred to the online
version of this topic.)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search