Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
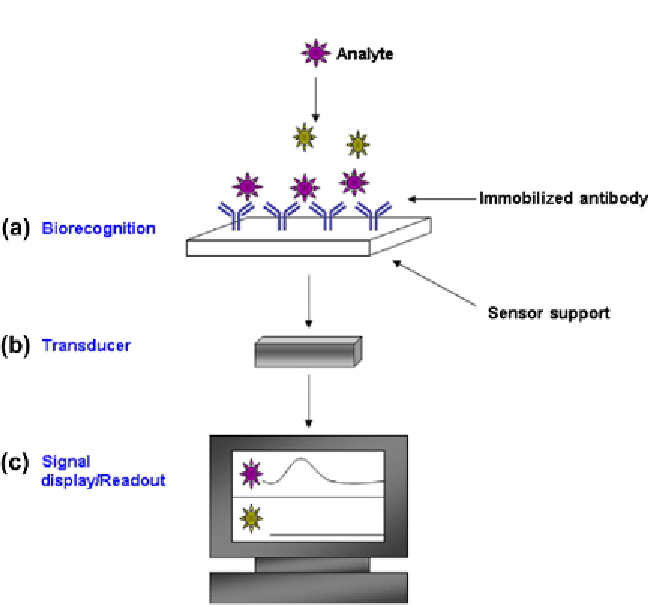
Figure 7.1
Biosensor components. (a) Analyte interaction with biorecognition element:
this is facilitated by the specificity of the immobilized antibody for its cognate antigen
(purple). Other biorecognition elements include enzymes, lectins, receptors, and micro-
bial cells. (b) Signal transduction: converts the interaction of the analyte molecule and
analyte into a quantifiable signal. (c) Readout or display: shows the specific signal gen-
erated by interaction with the analyte of interest. Yellow: nonspecific analyte. Source:
Figure 1 from Ref.
1
. Reproduced with permission.
(For interpretation of the references to
color in this igure legend, the reader is referred to the online version of this topic.)
This chapter aims to provide an introduction to biosensing technology
and review the applications for waterborne pathogens. The first sections of
the chapter present a background to biosensors classified under various tax-
onomies. Biosensors can be divided either by recognition element, by signal
transduction approach, or by direct or indirect detection techniques. Direct
detection biosensors are designed such that the biospecific reaction is directly
determined in real time. In indirect detection, the biosensor detects either
the presence of a secondary “label” added after the initial biorecognition step
or the products of that preliminary biochemical reaction. Finally, biosensors
can also be categorized into sensors operating in batch (intermittent) and
Search WWH ::

Custom Search