Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
19.1.5 Collisions Detection
Currently, the language only models bounding object collision detection with bound-
ing rectangles and bounding circles. An entity in the game model becomes a can-
with collisions, as is the case for the
ConditionalActuator CheckCollision
.For
Eberos GML2D, we only model two kinds of
BoundingObjects
:
BoundingRectangle
and
BoundingCircle
.The
BoundingRectangle
contains information about its
width and height in pixels. Similarly, the
BoundingCircle
contains information
about the size of its radius in pixels.
19.1.6 Input Handling
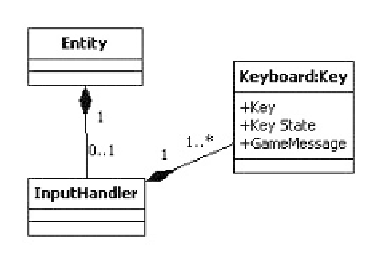
In Eberos GML2D, every entity reference is capable of having an
InputHandler
construct attached to it. When an entity has an
InputHandler
,itmeansthatsuch
an entity is controlled by an input device in some way. At the time this article was
written,
InputHandler
only models keyboard input.
Keyboard input is modeled by adding a
KeyboardKey
to the
InputHandler
con-
of information: the key to detect, the state of the key we are interested in, and
the
GameMessage
to dispatch when the key and key state are matched. Currently,
there are four possible states that can be modeled:
DOWN
,
RELEASED
,
WAS_PRESSED
,
and
IS_HOLDING
. Once the input is matched, that is, the key specified is in the de-
sired state, the entity attached to the
InputHandler
is notified of the
GameMessage
specified for that key. This
GameMessage
is then used as a link between the entity
logic and the input.
Figure 19.7.
Basic class diagram for entity to input relationship.