Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
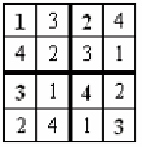
(b) Answers
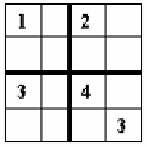
(a) 4*4 Soduku
Fig. 1.
4*4 Sudoku and the answers
tries to examine the information processing process of human problem solving
by the approach of combining computational cognitive model ACT-R (Adaptive
Control of Thought-Rational) and advanced fMRI (functional Magnetic Reso-
nance Imaging) brain imaging techniques [3, 5, 11].
In cognitive psychology and AI domains, many classical problem tasks have
been used to investigate the information processing processes of problem solving,
such as Tower of Hanoi, the savage and the missionary puzzle, and so on. These
tasks are somewhat complicated and cost long time to solve. A good task in
brain imaging experiments shall be solved in a short period with brief heuristics
and be consistent for all participants. We found that the simplified 4*4 Sudoku
is a good candidate with all these features. A 4*4 Sudoku, as shown in part (a)
of Figure 1, is a 4*4 matrix with two mid-lines bold lines are used to divide the
matrix which called boxes and some of grids are fill with digits. The task is to fill
all of the empty grids so that each row, each column, and each 2*2 box contains
the digits from 1 to 4 only one time each, as shown in part (b) of Figure 1. For
controlling the strategies that participants use, we simplified the problem so that
participants only need to find the answer in one grid which is marked by '?'.
2
Methods
2.1
Event-Related fMRI Experiment
Tasks
. As described in Section 1, we developed a new paradigm of human prob-
lem solving, simplified 4*4 Sudoku that involves seven heuristics which can be
classified into three groups.
-
The first three heuristics that are most easy one involve checking in one
dimension : (Row), (Column) and (Box). For example, Row heuristics is
shown in part (a) of Figure 2. Three digits in the set of 1 to 4 are given in
the row with grid of '?'. The answer of '?' is the resting digit.
-
The second three heuristics involve checking two dimensions: (Row and Col-
umn), (Row and Box), and (Column and Box). For example, Row and Col-
umn heuristics is shown in part (b) of Figure 2. Three digits in the set of 1
to 4 are given in the row and column with grid of '?'.