Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
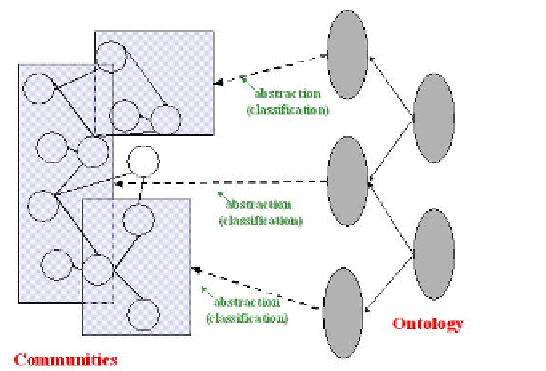
Fig. 4.
A collective intelligence built up from a community layer
intelligence are constantly creating new information, and are connecting up with new
nodes thus creating new communities.
In our model, we call
domain ontology
a directed graph
G
= (
C
,
R
) where nodes are
concepts and arches are binary relations. A
classifier
is a tuple (
TS
,
L
,
A
,
ϕ
) such that:
•
TS
is a training set of past cases
•
L
is a set of labels
•
A
is a set of actual cases
•
ϕ
:
A
→
L
is a
classification function.
Let
l
be a label in
L
. We call
seed relative to c
the set
-1
(
c
). Intuitively, in a Web con-
text the seed relative to the concept c is the set of URL's that are definitely about
c
.
Given a domain ontology
O
= (
C
,
R
), we perform
community trawling
upon
ϕ
-1
ϕ
(c) for each
c
in
C
. Community trawling is a process that, starting from a graph G,
finds all communities imbedded in the vicinity of G. See for example [11]. By doing
so, for each concept
c
C
, we obtain a set of graphs
C
(
c
) that represents a bundle of
Web communities pertaining to
c
.
∈
Example
Let{www.autopartsfair.com,www.griffinrad.com,www.radiator.com,www.carpartswh
olesale.com} be the set of URLs of the example in Figure 2. We now apply the algo-
rithm described in [11] to detect the Web communities subsumed by this set. The
Web community associated with the concept “Radiator” is individuated by the follow-
ing sites:
www.autoguide.net
www.autopartsfair.com
www.carpartswholesale.com