Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
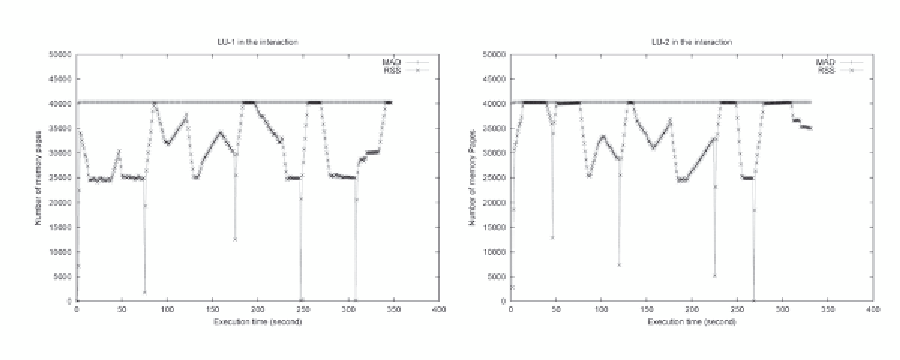
Figure 7. The memory performance of two LU programs in their concurrent execution.
•
When the memory demand of a process
frequency, are similar, false LRU pages
can be easily generated for both processes,
which can trigger the system thrashing. The
interactions between two
vortex
processes
in Figure 6 and between two
LU
processes
in Figure 7 are examples of this condition.
When the available memory space is sig-
has a sudden jump for additional memory
allocation, its RSS can be easily increased
accordingly at the beginning because ad-
dition of new pages do not need I/O op-
erations to access data on the disk (zero-
filled pages instead of disk-read pages).
If the process cannot establish its work-
ing set before many false LRU pages are
produced, the number of lost pages on the
false LRU condition can exceed the num-
ber of obtained pages through page fault-
ing, causing its RSS to drop. In addition,
the increased memory demand of this pro-
cess causes other processes in the system
to generate more false LRU pages. In this
way thrashing is triggered. The examples
of this condition include: the starting ex-
ecution stage of
gzip
in the left figure of
Figure 3, the second spike of
gcc
in the
bit-r
/
gcc
interaction in Figure 4, the first
spike of
gcc
in the
gcc
/
vortex
interaction
in Figure 5, and all the RSS jumps of both
LU
processes in Figure 7.
If memory access patterns of concurrently
•
nificantly less than the aggregate memory
demand of the processes, all the processes
compete for the limited memory alloca-
tions. A small number of page faults may
trigger a large number of false LRU pages.
This condition will be shown in Figure 8
before the token is taken by a process.
deSign and implementationS
of Swap toKen
We choose the Linux OS as a base to evaluate the
design and implementation of swap token. The
swap token has been implemented in Linux Ker-
nel 2.2 by Song Jiang and in Linux kernel 2.6 by
Rik van Riel. As a more thorough evaluation has
been conducted for the implementation in Kernel
2.2, the discussions on the topic in the chapter are
based on this implementation.
•
running programs, in terms of working set
size, memory usage behavior, and access
Search WWH ::

Custom Search