Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
Link
i
1
y
i
1
z
i
1
d
i
1
i
Link
i
x
i
1
z
i
y
i
x
i
i
1
a
i
Joint
i
1
Joint
i
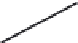
FIGURE B.28
DH parameters.
Table B.1
DH Joint Parameters for Joint
i
Name
Symbol
Description
Link offset
d
i
Distance from x
i-1
to x
i
along z
i
Joint angle
y
i
Angle between x
i-1
and x
i
about z
i
Link length
a
i
Distance from z
i
to z
iþ1
along x
i
Link twist
a
i
Angle between z
i
and z
iþ1
about x
i
Stated another way, the parameters that describe the relationship of the
i þ
1 frame to the
i
th frame
are a combination of
i
th joint parameters and
i þ
1 joint parameters. The parameters can be paired off to
define two
screw transformations
, each of which consists of a translation and rotation relative to a sin-
gle axis. The offset (
d
iþ
1
) and angle (
y
i
þ
1 joint relative to
the
i
th joint with respect to the
i
th joint's
z
-axis. The length (
a
i
) and twist (
a
i
) are the translation and
rotation of the
i þ
1) are the translation and rotation of the
i þ
i þ
1 joint's frame from the
i
th frame can be constructed from a series of transformations, each of which
corresponds to one of the DH parameters. As an example, consider a point,
V
iþ
1
, whose coordinates are
given in the coordinate system of joint
i þ
1. To determine the point's coordinates in terms of the coor-
the parameter specifies the amount of rotation or translation, and the subscript specifies the axis
involved. The matrix
M
maps a point defined in the
i þ
1 frame into a point in the
i
th frame. By forming
the
M
matrix and its inverse associated with each pair of joints, one can convert points from one frame

















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search