Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
100
80
60
P
y
rolyzing
C
o
mbustion
40
20
0
700
800
900
1000
1100
1200
Temperature (°C)
Fig. 4.4
Effect of temperature on Hg
0
during pyrolyzing and burning
100
80
60
Com
b
ustion
Pyrolyzing
40
20
0
700
800
900
1000
1100
1200
Temperature (°C)
Fig. 4.5
Effect of temperature on Hg
2+
during pyrolyzing and burning
During pyrolyzing, Hg
0
reaction functions with Cl from Cl
2
and HCl in flue gas
were concluded as follows:
0
(4-1)
Hg
Cl
HgCl
(g)
2(g)
2(s,g)
0
Hg
2HCl
HgCl
H
(4-2)
(g)
(g)
2(s,g)
2(g)
0
Hg
Cl
HgCl
(4-3)
HgCl
Cl
HgCl
(4-4)
2
HgCl
HCl
HgCl
H
(4-5)
2
HgCl
Cl
HgCl
Cl
(4-6)
2
2
During burning, Hg
0
reaction functions in the flue gas were concluded as follows:
2Hg
澠澡
O
2HgO
澠 澡
(4-7)
g
2
s,g
0
(4-8)
2Hg
4HCl
O
2HgCl
2H O
(g)
(g)
2(g)
2(s,g)
2
(g)
0
4Hg
4HCl
O
4HgCl
2H O
(4-9)
(g)
(g)
2(g)
2
(g)
Both HgO and HgCl
2
generated in the reaction, Eqs. (4-7), (4-8) and (4-9), were
compounds of Hg
2+
. When the temperature reached more than 300 °C, the positive

















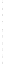


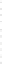






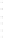

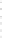





















































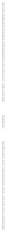








Search WWH ::

Custom Search