Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
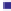
40
30
20
Coal consumption
Mercury emission
10
0
2005
2025
2010
2015
2020
-10
-20
Year
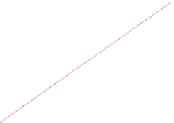
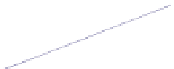
Fig. 3.4
Growth rates of coal consumption and mercury emissions of coal-fired power plants in
China from 2005 to 2020
3.5 Summary
Estimating mercury emissions is the first step in understanding the current situation
of mercury pollution in China, conducting research on mercury pollution control,
and developing emission control methods. In this section, with a focus on the es-
timation of mercury emissions as well as data for coal consumption and various air
pollution control facilities in China, we accurately estimated mercury emissions in
recent years and made a prediction for the development of mercury control ap-
proaches in China.
From 2000 to 2002, the growth rate of mercury emissions from coal-fired power
plants in China was estimated to have accelerated by 10%. From 2002 to 2005, the
growth rate increased to 12%. Increased ESP could effectively reduce mercury
emissions into the atmosphere. Moreover, desulfurization equipment WFGD could
remove most of the mercury in an oxidized state by washing.
In 2007 and 2008, mercury emission of coal-fired power plants in China was
predicted to reach 161.3 and 172.2 tons, respectively. By 2010, the proportion of
FGD equipment would increase to 50%. Meanwhile, the SCR configuration in-
creased from 1% in 2007 to 5% in 2008. Mercury emissions of all coal-fired power
plants comprised only 179.4 tons. In 2020, the ratio of FGD equipment was ex-
pected to increase from 50% in 2010 to 70%, whereas the SCR equipment was
expected to increase from 5% in 2010 to 10%. The mercury emissions of all
coal-fired power plants could reach a total of 207.0 tons by that time.
Although coal consumption in thermal power plants was predicted to increase
over the next decades, the controlled volume of mercury emissions of coal-fired
power plants could offset the increased volume of coal consumption of thermal
power plants, even leading to declining mercury emissions. This might be possible
due to the increase in coal washing practice and the extensive use of flue gas
cleaning devices. In the future, improvement in the proportion of coal after washing
and the extensive use of flue gas control devices, including desulphurization and























Search WWH ::

Custom Search