Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
8
14
7
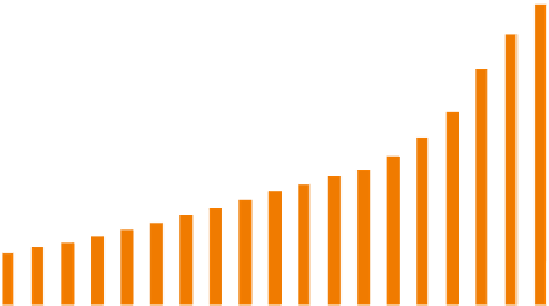
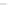
Total installed capacity of power
12
6
Total installed capacity of coal-fired power
10
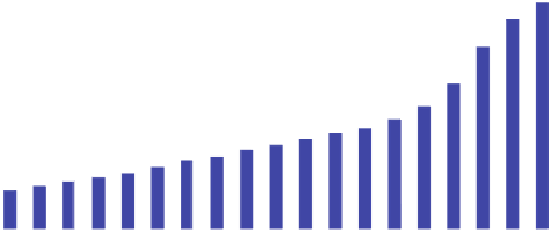
Total coal consumption of coal-fired power
5
4
8
3
6
2
4
1
2
0
Year
Fig. 1.2
Capacity and coal consumption of electric power generation in China from 1990 to 2008
Conventional pollutant emission control technologies for particles SO
2
and NO
x
has progressed in recent years in China. Currently, most coal-fired power plants are
equipped with dust-cleaning equipment
ˈ
such as electrostatic precipitators (ESP) or
fabric filters (FF). Desulfurization technology has also rapidly developed
[8]
. In
2005, the capacity of coal-fired power plants equipped with a desulfurization unit
was 12.3%. However, in 2009, this capacity was about 78% (about 470.0 GW). In
addition, SO
2
emissions from coal-fired power plants appeared to have decreased
for the first time. Wet limestone-gypsum desulfurization is mainly used as flue gas
desulfurization technology in China. By 2007, 26 sets of flue gas NO
x
-controlled
devices had been installed in coal-fired power plants in China, with a total capacity
reaching 11,250 MW. Most power plants used selective catalytic reduction (SCR)
technology, except four units of 600 MW that adopted selective non-catalytic re-
duction (SNCR). At present, nearly 200 sets of NO
x
-controlled devices for 105.0
GW capacity have passed environmental assessments
[9]
. Given the rapidly in-
creasing demands for environmental protection requirements, more coal-fired units
must be equipped with flue gas desulfurization and NO
x
-controlled devices.
However, although these conventional pollutant control technologies can affect
gaseous mercury (Hg
(g)
) emissions, the ability to control Hg
(g)
depends on mercury
speciation.






























































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search