Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
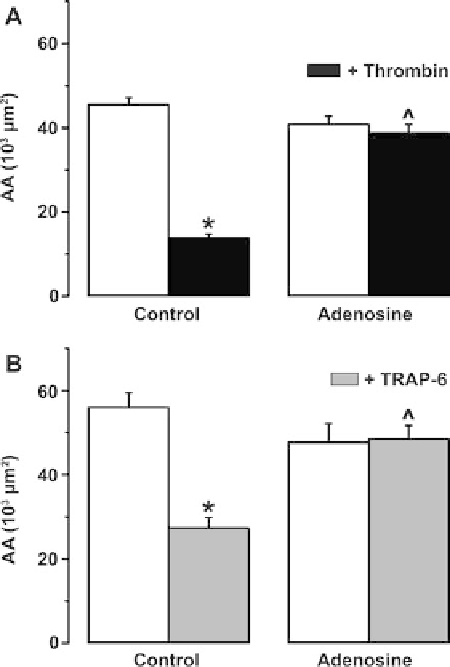
Fig. 10.8
Effect of PAR-1 receptor agonists on the active area of the Ca
2+
wave in control and
in cells pretreated with adenosine. The
bar graphs
in the
left panels
show the reduction of the
activearea(AA)oftheCa
2+
wave propagation by thrombin (2 U/ml for 5 min;
N
=
145) (
a
)
andbyTRAP-6(10
25) (
b
): The
bar graphs
in the
right panels
show the
inhibition of the effect of thrombin and TRAP-6 by pretreatment of the cells with adenosine (200
μ
μ
M for 30 min;
N
=
M for 30 min)
∗
p
< 0.001 for comparison between aa in the presence vs. absence of the PAR-
1 agonist (i.e., comparison of
black or grey bars
with
white bars
in each condition). ˆ
p
< 0.001
for comparison between AA in the presence vs. absence of adenosine (i.e., comparison of filled
(
black
respectively
grey
) bar with corresponding
filled bar
in control condition. From [27] with
permission. Copyright:
Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology
recovery in FRAP experiments, indicating an effect on GJIC, the main effect of these
agents was a reduction of PIC. Activation of PAR-1 did not significantly affect the
Ca
2+
wave propagation in cells pretreated with the hemichannel blocker
43
Gap26
or in the presence of exogenous apyrases. Thrombin abolished enhancement of the
Ca
2+
wave propagation by the ectonucleotidase inhibitor ARL-67156 [26]. These
experiments demonstrate that the effect of thrombin on Ca
2+
wave propagation is
mainly due to inhibition of purinergic PIC.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search