Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
(along an osmotic gradient driven by the active secretion of Cl
−
ions ) was
dependent upon the 5
ectonucleotidase [71]. Thus, it was concluded that luminal
ATP-derived adenosine represents a tissue-adaptive response during inflammation
which may represent a mechanism for flushing of potentially harmful pathogens at
from the surface of the mucosa (Fig. 8.1).
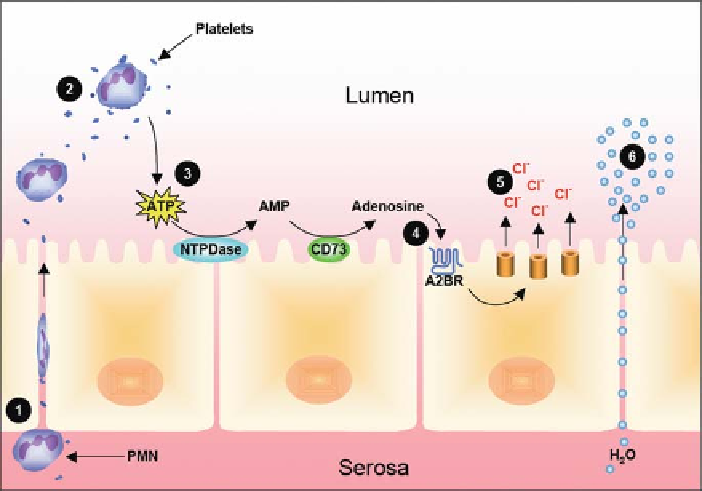
Fig. 8.1
Model of facilitated platelet translocation and activation of epithelial electrogenic Cl
secretion during PMN transmigration
:
During active inflammation, platelets are caught in the
flow of PMN transmigration, resulting in platelet translocation across the apical side of mucosal
epithelial cells (1). PMN and platelet-derived ATP (2) is selectively metabolized to adenosine by a
two-step enzymatic reaction involving ecto-apyrase and ecto-nucleotidase (CD73) (3). Adenosine
binding to apical adenosine A2B receptors (4) results in activation of electrogenic Cl secretion and
the paracellular movement of water (6). Such platelet/PMN - epithelial crosstalk pathway may
serve as a defensive response by which mucosal surfaces are flushed from bacteria and bacterial
products under inflammatory conditions. Figure adapted from Weissmuller et al. [71]
8.4 Transcriptional Regulation of CD39, CD73 and Adenosine
Receptors
It is well appreciated that under levels of low oxygen tension (
pO
2
), extracellular
adenosine levels are increased [17, 59]. It is in this hypoxic microenvironment that
a wide range of genes is upregulated under the control of the transcription factor
hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) [55, 56]. HIF-mediated signaling represents a rel-
atively rapid adaptive mechanism to low oxygen conditions within the ischemic
Search WWH ::

Custom Search