Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
DSCP
DSCP, which is defined in RFC 2474, provides for 64 values (2
6
) for prioritization by using the
six most-significant bits of the IP ToS field. DSCP replaces the ToS field with the DSCP field,
as shown in Figure 11-5. You can use DSCP for packet classification for later policing. With
DSCP, service providers can classify packets into more service levels (CoS) than the eight
levels possible with the IP Precedence bits.
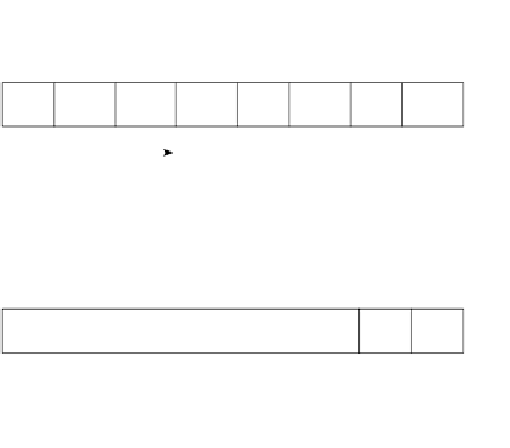
DSCP Field Replaces the ToS Field
Figure 11-5
8-bit IPv4 Type of Service Field
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
Precedence
Bits
DSCP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
DSCP bits
UU
U = unused
Consult RFC 2474, “Definition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field) in the IPv4 and
IPv6 Headers,” for more information on DSCP.
Network-Based Application Recognition (NBAR)
NBAR is a Cisco IOS feature that provides classification of network applications. NBAR marks
packets in the ToS or DSCP field so that other QoS mechanisms can prioritize traffic. The
advantage of NBAR is that it is preconfigured with network applications so that the network can
automatically classify (mark) packets.
For more information and configuration examples, go to the following site: www.cisco.com/
warp/public/cc/so/neso/ienesv/cxne/nbar_ov.htm.
PoS and IP Precedence
POS/Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) technology removes the ATM layer (IP/ATM/
SONET) between IP and SONET. This permits the ability to configure IP QoS mechanisms on














Search WWH ::

Custom Search