Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
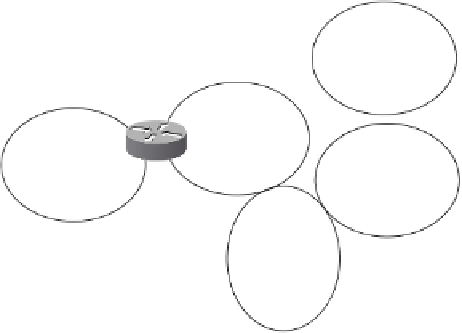
OSPF Areas
Figure 8-1
Area 3
Area 0
Area 1
Area 2
Area 4
Intra-area traffic consists of packets that are passed between routers in a single area. Intra-area
traffic is routed within an area based on the routing table that is built from information learned
through Type-1 and Type-2 LSAs. Interarea traffic is passed between routers in different areas.
Type-3 and Type-5 LSAs are flooded throughout all areas, and advertise IP network addresses
that are located in other areas and autonomous systems. These addresses are added directly to
each router's routing table, without forcing the router to run the SPF algorithm first.
OSPF Router Types
OSPF defines several router types that are related to their place and function in the area
architecture. Figure 8-2 shows a diagram of OSPF router types.
The following is a list of explanations for each router type in Figure 8-2:
•
Internal router
—Interface belongs to the same OSPF area and keeps only one link-state
database.
•
Area border router (ABR)
—Connects to more than one area; maintains a link-state
database for each area that it belongs to and generates summary LSAs.
•
Autonomous system boundary router (ASBR)
—Inject external LSAs into the OSPF
database. External routes are learned either through other routing protocols or static
routes.
•
Backbone router
—Has at least one interface attached to area 0.
A router can be an ABR, ASBR, and backbone router at the same time.















Search WWH ::

Custom Search