Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
reliability and maintaining the original simplified modeling approach at the same
time.
The model fundamental assumption is the canopy LUE (light use efficiency)
approach, considering the GPP as the product of the absorbed photosynthetically
active radiation (aPAR) and
ʵ
max,
which is assumed to be a biome-specific con-
stant for potential LUE (g C m
−
2
MJ
−
1
), and reduced by the effect of environ-
mental constraints (
f
(
x
)
). Daily GPP (g C m
−
2
MJ
−
1
) has then been computed as
follows:
GPP
=
aPAR
× ε
MAX
×
f
(
x
)
(5.4)
The model reduces daily potential GPP by the effect of environmental constraints
represented by four modifiers, ranging between 0 (system “shutdown”) and 1 (no
constraint). Main environmental modifiers are daily average temperature (T) modi-
fier (
f
T
), daily VPD modifier (
f
D
), soil water modifier (
f
ʸ
) and light modifier (
f
L
).
Effects of daily average temperature on daily GPP have been modeled as a func-
tion of cardinal temperatures, minimum (T
(Tmin),
), maximum (T
max
) and optimum
(T
opt
) temperature for net photosynthetic production, as proposed by Sands and
Landsberg (
2002
). Other environmental modifiers have been calculated according
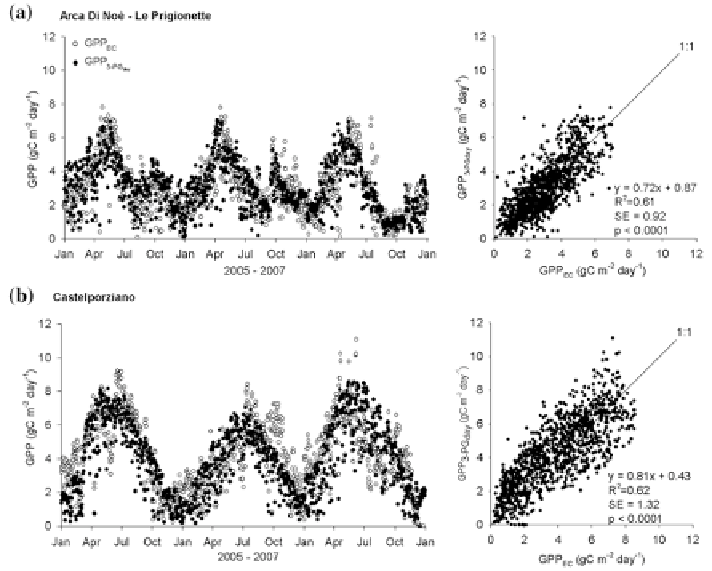
Fig. 5.3
EC measured and 3PG estimated GPP daily patterns for:
a
Arca di No│-Le Prigionette
(2005-2007);
b
Castelporziano (2005-2007) (Nol│ et al.
2013
)