Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
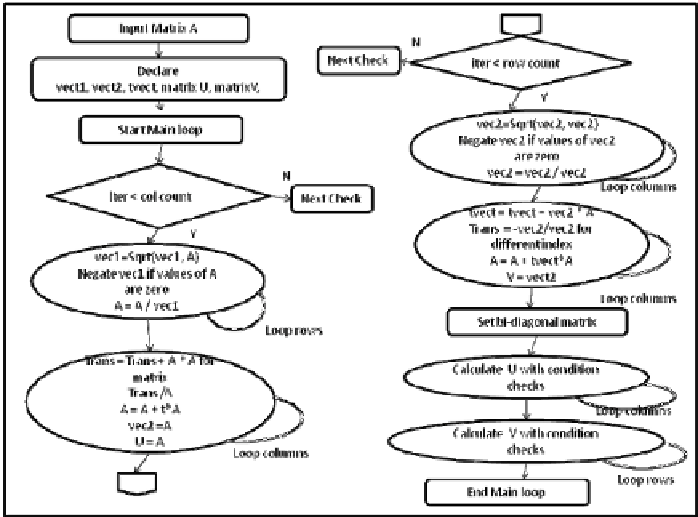
4.
Find the ith row transformation and place the ith super-diagonal in
vector2, Apply transformation
5.
Store the transformation in V
6.
Order the Matrix to bi-diagonal form, storing the diagonal elements in
vector1 and the super-diagonal element in another vector2
7.
Generate U
8.
Generate V
The
Fig. 2
gives the overview of Bi-diagonalization design and
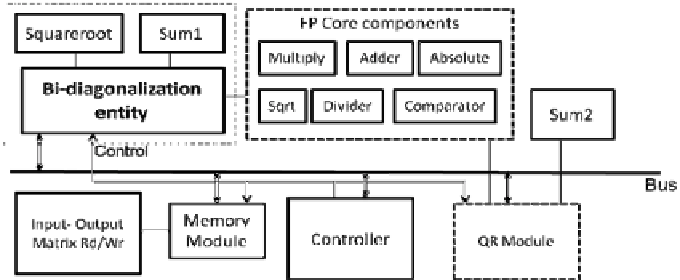
Fig. 3
gives
Bi-diagonalization entity RTL view and SVD implementation. To our knowledge Bi-
diagonalization architecture is not available in literature and comes as our
contribution.
Fig. 2.
Overview of Bi-diagonalization design and implementation
Fig. 3.
Bi-diagonalization entity RTL view and SVD Implementation