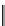Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
2
2
2
V
V
V
n
,
X
4
n
,
Xo
n
,
X
2
V
2
V
n
,
M
4
,
2
V
M
,
2
V
,
2
2
V
V
n
,
Rs
n
,
X
2
Fig. 5.
Major noise sources of UWB LNA
γ
g
m2
R
ʱ
2
R
1
R
g
m2
X
1
2
ʱ
2
+
F
z'
= 1+
(4)
(5)
F = 1 + (F
z
-1) + (F
z'
-1)
R
2
4R
g
m1
X
o
2
R
s
R
4
g
m1
g
m4
X
o
X
4
2
R
γ
g
m1
X
o
2
g
m4
R
ʱ
2
ʱ
2
F = 1+
+
+
+
(6)
R
1
R
g
m2
X
1
2
ʱ
2
+
Equations (7) and (8) describe the noise of M1 at z and z' respectively. The factor
r
is
defined as the ratio of these two noise factors as given in (9). For the condition of
complete noise cancellation, the value of
r
should ideally be equal to 1. Thus, the
factor
r
signifies the fraction of noise of M1 cancelled at the output.
2
4kTγ
g
X
m1
o
−
(
)
(7)
g
1
+
g
R
||
X
m1
m1
s
2
Noise
factor
of
M1
at
z
=
(
(
))
2
g
X
||
r
4kTR
m1
o
o1
s
2
4kTγ
X
||
R
2
s
(8)
g
R
||
X
+
1
g
m1
s
2
m1
Noise
factor
of
M1
at
z'
=
4kTR
s
r
Noise of M1 at z
Noise of M1 at z'
(9)