Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
1.005
1.00
Propagation delay
Leakage current
1.000
Propagation delay
Leakage current
0.95
0.995
0.990
0.90
0.985
0.85
0.980
0.975
0.80
0.970
0.75
0.965
0.960
0.70
1.85
1.90
1.95
2.00
2.05
2.10
135
136
137
138
139
140
Oxide thickness (nm)
PMOS width (nm)
(a) (b)
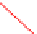
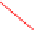
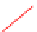
Fig. 2.
Variation of propagation delay and leakage current with (a) oxide thickness and (b)
width of PMOS transistor
Table 1.
Variation of leakage current and propagation delay for different
T
ox
of a PMOS
transistor
T
ox
variation
(nm)
Leakage
current (nA)
Propagation
delay (ns)
1.85
8.582
0.0987
1.90
8.069
0.0991
1.95
7.594
0.0996
2.00
7.156
0.1001
2.05
6.748
0.1007
2.10
6.370
0.1014
Table 2.
Variation in leakage current and propagation delay for different
widths of PMOS
transistor at
T
ox
= 2nm
Width of PMOS
transistor (nm)
Leakage
current (nA)
Propagation
delay (ns)
135
7.1557
0.1001
136
7.2129
0.0994
137
7.2702
0.0987
138
7.3275
0.0980
139
7.3847
0.0978
140
7.442
0.0967
3.2
Analysis of Leakage Current for Gate Replacement Using Dual-
T
ox
Transistors
Once the value of
T
ox
has been chosen, the modified gate replacement algorithm is
applied wherein the gates can be replaced with another gate. This replaced gate
incorporates an extra sleep signal along with PMOS transistors with higher value of
T
ox
. As presented in Table 3, while the variation of
T
ox
is applied to a circuit, it will not