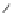Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
and SMG DGJLT. The value of G
D
for DM-DGS, DMG and SMG DGJLT are 1.42
mS, 1.4 mS and 1.25 mS respectively at V
GS
=0.2 V. However, G
D
decreases with gate
voltage because of higher mobility and hence more collisions. Early voltage (V
EA
)
with respect to V
GS
is also shown in fig. 5. Early voltage can be derived from output
resistance and vice versa as
V
EA
= R
O
I
D (sat)
or, I
D
/G
D
(2)
Where, I
D (sat)
is the saturation current. After a gate voltage of ~ 0.5 V, DM-DGS has
higher early voltage followed by DMG and SMG DGJLT. At a gate voltage of 1 V, the
values of V
EA
are 97 V, 86 V and 14 V for DM-DGS, DMG and SMG DGJLT
respectively. Like G
D
, early voltage at lower V
DS
is dominant by CLM and at higher V
DS
,
it is dominant by DIBL. The better performance of DM-DGS is attributed to the superior
vertical gate coupling as well as lesser lateral drain control on drain current [11].
The intrinsic gain (A
V
) with respect to V
GS
is also plotted in fig. 5. The intrinsic
gain of a device can be written as
V
(3)
A
= G R
or, G
EA
V
mO
m
D (sat )
I
Dual metal gate devices offer higher
A
V
in comparison to single metal gate devices
because of higher transconductance as well as output resistance for aforementioned
reasons.
The gain values for DM-DGS, DMG and SMG DGJLT are 50.1dB, 51.8 dB,
39.5 dB at V
GS
=0.2 V; and 35.5 dB,31.5 dB and 27.2 dB at V
GS
=1 V respectively.
400
DMG
DM-DGS
SMG
300
200
100
0
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
Gate Voltage, V
GS
(V)
Fig. 7.
Cut-off frequency (f
T
) with respect to gate voltage for the devices at V
DS
= 1 V for L
=40 nm, T
si
=8 nm and T
ox
=2 nm
The unity-gain cut-off frequency (f
T
) is another figure-of-merit useful for analog
applications. It is given by [19]
G
(4)
f
=
m
T
(
)
2C C
π
+
GS
GD