Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
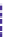
The TajMahal image
not just even ones. The most basic definition is a little messy. For each integer
k
≥
0, define
a
k
=
1
2
f
(
x
)cos(
kx
)
dx
and
(18.40)
−
1
2
b
k
=
1
2
f
(
x
)sin(
−
kx
)
dx
.
(18.41)
1
2
−
Notice that
b
0
is always 0.
The sequences
Frequencies less than 15
(low frequency)
{
a
k
}
and
{
b
k
}
are called the Fourier transform of
f
.If
f
is
continuous and
f
(
2
)=
f
(
1
−
2
)
, then it turns out that
∞
f
(
x
)=
a
k
cos(
kx
)+
b
k
sin(
kx
)
.
(18.42)
k
=
−∞
Surprisingly, the annoyance of having an unnecessary value (
b
0
), the vague-
ness of “the Fourier transform consists of two sequences,” and the somewhat sur-
prising appearance of the negative sign in the definition of
b
k
can all be resolved
by generalizing to complex numbers.
Instead of real-valued functions
f
:[
1
2
,
2
]
→
R
, we'll consider complex-
valued functions. And instead of considering the sine and cosine separately, we'll
define
−
Frequencies 15 to 70
(middle frequency)
kx
)=
e
2
π
i
kx
.
e
k
(
x
)=cos(
2
π
kx
)+
i
sin(
2
π
(18.43)
Inline Exercise 18.3:
Show that
(
e
k
(
x
)+
e
−
k
(
x
))
/
2
=cos(
2
π
kx
)
, and
(
e
k
(
x
)
−
e
−
k
(
x
))
kx
)
, so that any function written as a sum of sines and
cosines can also be written as a sum of
e
k
s, and vice versa.
/
(
2
i
)=sin(
2
π
Frequencies greater than 70
(high frequency)
The only other change is that the definition of the inner product must be
slightly modified to
=
f
(
x
)
g
(
x
)
dx
,
f
,
g
(18.44)
where
a
+
b
i
=
a
b
i
is the
complex conjugate.
Making this change ensures
that the inner product of
f
with
f
is always a non-negative real number so that its
square root can be used to define the length
−
.
With this inner product, the set of functions
f
{
e
k
:
k
∈
Z
}
is
orthonormal,
that is,
Figure 18.36: The low-, middle-,
and high-frequency components
of the Taj Mahal image.
=
0
j
=
k
e
k
,
e
j
j
=
k
;
(18.45)
1
1
the proof is an exercise in calculus and trigonometric identities.
We define
0
−
5
0
5
c
k
=
1
2
f
(
x
)
e
k
(
x
)
dx
=
f
,
e
k
.
(18.46)
Figure 18.37: A function with
equally spaced peaks that fade off
as x
−
1
2
→±∞
.