Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
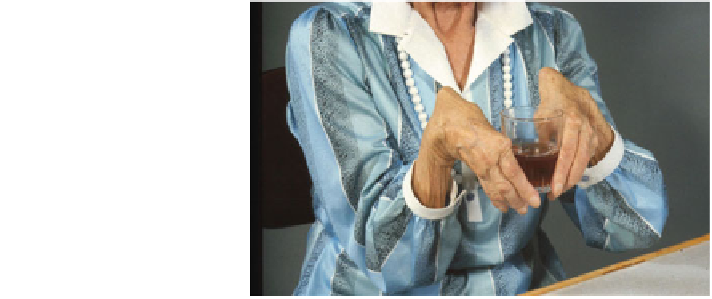
Fig. 3.1 Patient affected by
rheumatoid arthritis with
severe dislocation of both
wrists [
10
]
was defined as worn off of the articular cartilage in any portion of the bones which
gives exposure to the subchondral bone. This study has reported that 58 % of the
specimens suffered with arthrosis; 21 % of them were identified at the radiocarpal
joint whereas 46 % was observed at the midcarpal joint. 24 % of the dissected
specimens were found to have chondromalacia, which were found to have
disabnormalities of softening and fibrillation associated with articular cartilage.
Out of that, 4 and 22 % were affected by the disease at the radiocarpal and
midcarpal joints, respectively.
All of these reported findings showed high frequency of tissue damages, thus
significantly indicate that numerous wrist joints are over worn or overloaded
during their lifetime. This phenomenon is worsening as the aging population is
increasing thus leading to higher demands in the future. However, treatments'
options are fairly limited and less efficient due to the weak understanding towards
the biomechanical behaviour of the wrist, as well as limited computational and
experimental resources. Carpectomy, partial or complete arthrodesis and arthro-
plasty are examples of available treatments [
2
-
9
]. Each of them nonetheless has
their own weaknesses. For instance, the limited motions due to bone fusions in
arthrodesis resulted in less independencies of the patient. The arthroplasty as
another option experiences high failure rates [
8
].
3.2 Rheumatoid Arthritis
One of the most common skeletal diseases associated with the wrist joint is rheu-
matoid arthritis (RA) [
10
,
11
]. The disease affects mostly synovial joints, resulting
in considerable pain, loss of function and eventual deformity as shown in Fig.
3.1
.It
is a life-long condition, and the disease activity might change over time. Rheu-
matoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic, inflammatory disease that results from an
autoimmune disorder causing the damage of the joint [
12
,
13
]. Swelling and
inflammation of the joint are as a result of lymphocytes effect in the synovium,
leads to mutilation of the joint. RA as a symmetrical disease is normally attacks
Search WWH ::

Custom Search