Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
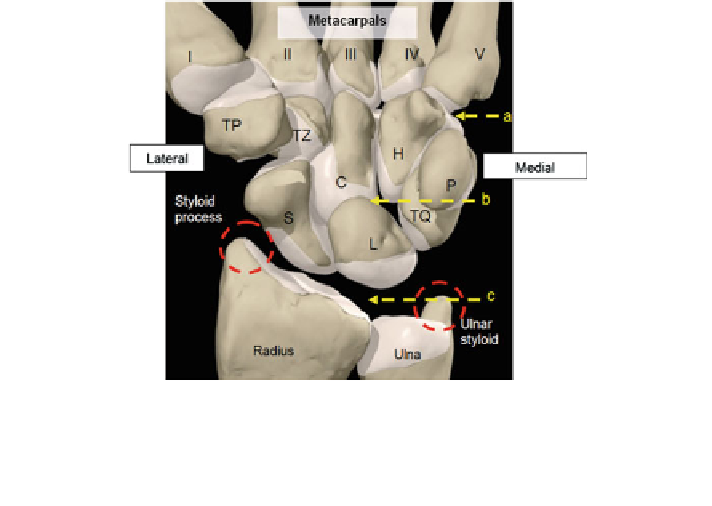
Fig. 1.1 Schematic drawings for palmar view of the wrist joint complex showing the eight
carpal bones and their articulations with the distal radius, distal ulna, the metacarpal bones of the
hand and each other. H hamate, C capitates, TZ trapezoid, TP trapezium, TQ triquetrum,
P pisiform, L lunate, S scaphoid. The arrows indicate the line of the joints. a carpometacarpal;
b midcarpal; c radiocarpal. The light brown surfaces indicate the articular cartilages [
8
,
9
]
The carpus is divided into the proximal and distal row. The bones of the distal
row from the radial to ulnar side are the trapezium, trapezoid, capitate and hamate.
The distal carpal row forms a relatively immobile transverse unit that articulates
with the metacarpals to form the carpometacarpal joint. All four bones in the distal
row fit tightly against each other and are held together by stout interosseous
ligaments [
1
,
2
]. The more mobile proximal row consists of the scaphoid, lunate,
and triquetrum. This row articulates with the distal radius to form the radiocarpal
joint (scaphoid fossa of radius, 46 %; lunate fossa of radius, 43 %; ulnar soft tissue
structures, 11 %). The scaphoid connects anatomically and functionally both rows,
and articulates in part with the radius. The lunate articulates in part with the ulnar
soft tissue structures. The eighth carpal bone, the pisiform is a sesamoid bone that
mechanically enhances the wrist's most powerful motor, the flexor carpi ulnaris,
and forms its own small joint with the triquetrum. Between the proximal and distal
rows of carpal bones is the midcarpal joint, and between adjacent bones of these
rows are the intercarpal joints. The wrist consists of three main joints; distal
radioulnar joint, the radiocarpal joint, and the midcarpal joint. The palmar surface
of the carpus as a whole is concave, constituting the floor and walls of the carpal
tunnel. The complete anatomy of the wrist joint is illustrated in Fig.
1.1
.
The radiocarpal joint, which is arguably the most critical articulation in the
wrist joint [
2
-
4
] consists of 75 % of the articulation between proximal carpal
bones and the distal radius, whereas the remaining 25 % is the ulnacarpal or in
particular, triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) together with two main
facets:
elliptical
scaphoid
facet
and
spherical
lunate
facet
[
5
].
There
is
a
Search WWH ::

Custom Search