Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
2.3 Design of structures: an introduction
The following section provides a brief illustration into how engineer-
ing projects are designed and constructed, so that the following chap-
ters dealing with ground investigation and preparation of ground
models can be better understood. The project types used for this
introduction are a) foundations for a building and b) tunnels. Civil
engineering design and construction is addressed in more detail in
A building imposes a load on the ground. This will include the vertical
dead weight of the building
fittings and a live load
including transient loads such as from snow, wind or earthquake
loading, as discussed in detail in
Chapter 6.
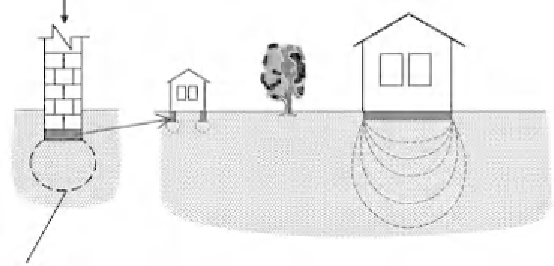
The stress from a building,
if placed directly on to
-
its walls and
xed
flat, essentially isotropic ground, will decrease
with depth and can be expressed as a bulb of pressure, as illustrated in
Figure 2.3.
At a depth of perhaps 1.5 to 2.0 times the diameter of a
building, the stress level can be anticipated to reduce to 10% of the
stress immediately beneath the foundation (Tomlinson, 2001). This is
an important rule-of-thumb for the engineering geologist to keep in
mind because it gives an indication of the minimum depth of ground to
be investigated, as discussed in
Chapter 4.
The depth of signi
cant
stress change also depends upon the nature of the foundations
required, as illustrated in
Figure 2.3.
Figure 2.3
The
concept of a stress
bulb beneath a
structure. This is
based on elastic
analysis of uniform
materials, but is
indicative and
helpful. The wider
the structure, the
greater the volume
of ground that will
be stressed
signi
Shallow foundation
on soil
soil
Small house on strip
footings beneath load
bearing walls only
stresses ground locally to
shallow depths
Large building founded
on a raft to spread the
load, (with reduced stress)
but stresses are carried by
a much larger volume
beneath the building
Stressed
zone