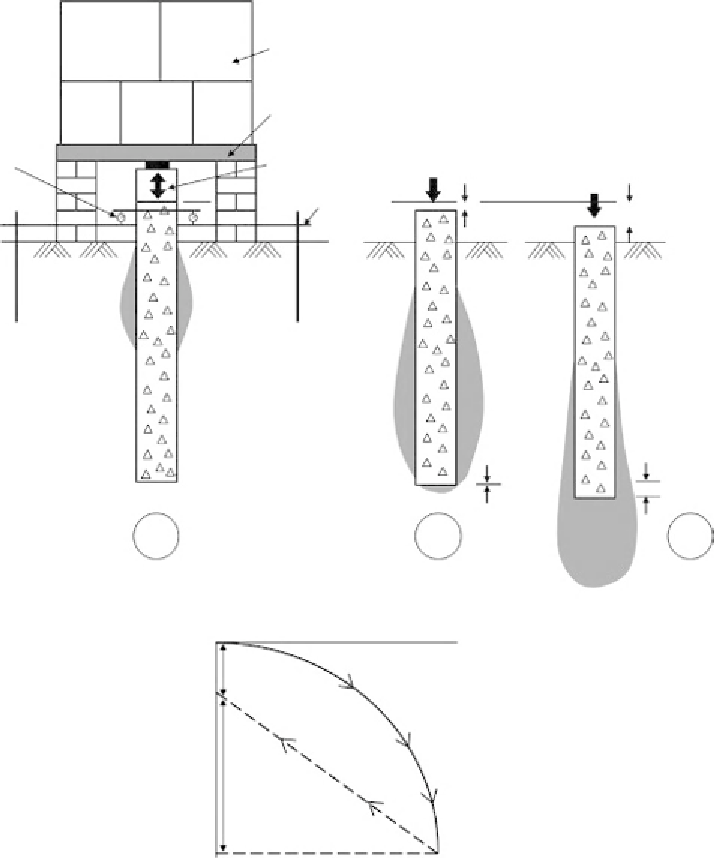
Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
Reaction dead
weight
(kentledge)
Spreader beam
Displacement
measurement
Jack and load
measurement
Reference
beam
Displacement
Support for
reference
beam away
from test
Most of
load in
skin
friction
Load carried
by skin
friction at
higher level
Skin friction
reduced to
'residual'
1
2
3
End bearing
failure
Load
1
2
3
Residual
settlement on
removal of
load
settlement at
top of pile
'Elastic'
settlement of pile
and ground
Figure 6.10
Typical set-up for pile load test. At early stages (1), most of the ground resistance will
come from skin friction at shallow depths. End bearing is not mobilised until later stages (2) and (3)
of the test (depending on the con
le). The rate of settlement
increases as the ground resistance becomes fully mobilised and there will be some permanent
displacement (residual settlement) once the pile is unloaded.
guration of the pile and ground pro
performing until a test approaches failure (
Figure 6.10)
. Recently, a
system has been introduced where Osterberg cells are incorporated
into the pile construction at depth and then expanded against the test
pile, both upwards and downwards
(Figure 6.11).
The end-bearing
resistance below the cell is balanced by the skin friction from the soil
above the cell. This systemwas used for the Incheon Bridge design, using