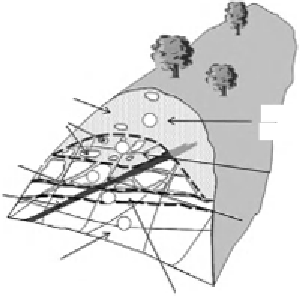
Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
saprolite
corestones
saprolite
orestones
Unit 5 mostly
saprolite
Unit 5
sapro
5
5
4
4
adverse joints
joints
Unit 4 significant proportion
of corestones
Uni
of c
3
3
dyke
2
2
Unit 3 More than
50 % rock
Unit 3
50 % r
1
1
Unit 1 good
quality rock
Unit 1 good
quality rock
Unit 2 weathering
on joints
Uit2
th
i
Figure 3.61 A schematic ground model for a weathered rock slope with units de
ned by degree of
faults and adverse master joints, need to be included as individual entities.
Figure 3.62
Preliminary ground
model for
foundation design,
with key geological
elements identi
ed
for geotechnical
characterisation re
physical parameters
and behaviour.
Unit 1
Compressible
clay
Unit 2
Dense sand
Unit 3
Weathered
rock
Unit 4
Strong rock
The model with assigned geotechnical parameters becomes a design
model, which is then used to predict the interaction between the
structure and the ground, for example, from a building load, to
ensure that failure will not occur (ultimate limit state) and that defor-
mation will be within the tolerance of the structure (serviceability limit
state). It must allow failure and deformation mechanisms to be