Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
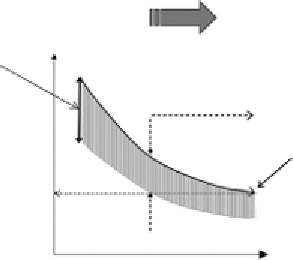
STABLE
UNSTABLE
Temporary
reduction of
F of S in severe
storm
Possible partial
movement during
storm
F of S
Slope fails even
under dry
conditions
1.0
Slope stable
even under
severe storm
Gradual deterioration of slope over time (say 1,000 years)
some stage, the slope will reach the point where it may be moved a little by some transient process
such as intense rainfall or an earthquake. Deterioration will then continue and probably accelerate
until eventually full detachment occurs. As Hencher (2006) notes, hillsides can be regarded as having
an inventory of different parcels of ground, all at different stages of deterioration and, therefore,
susceptibility to a particular triggering event. Depending on the severity of the event, one, two or
many landslides will occur.
Volcanic risk is a clear problem, but sources of the hazards are gen-
erally well known, although surprises do occur, as in the case of the
mud volcano that erupted disastrously in 2006 (Davies et al., 2011).
Clearly, if a volcano is active then construction should avoid the
potential zone of travel and deposition of very hazardous materials
such as lava and ignimbrite. Landslides associated with volcanoes are
called lahars, which can travel great distances and be hugely damaging.
Noxious gases are produced by volcanic activity. A tragic case at Lake
Nyos in Cameroon, Africa, in 1986, involved the eruption of a bubble
of carbon dioxide that suffocated more than 1,700 people and 3,500
livestock in nearby villages. Avoidance is again the only real option.
Earthquakes are rather more of a general hazard in that they can
occur anywhere in the world, though seismic activity is concentrated
along active plate boundaries. The process of assessing earthquake
hazard for a site and then design to withstand the potential shaking
are dealt with in
Chapters 4
an
d 6.
3.8.1 Introduction
Ground modelling is an essential part of engineering design. The
ground model for a project will mainly comprise a simpli
ed repre-
sentation of the site geology that should include all aspects that are
likely to affect the project or to be affected by the project. A useful