Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 1.
Region of interesting (ROI) extracting
Circle Projection Histogram
θ
=0
100
50
0
(a)
100
150
200
250
300
Circle Projection Histogram
θ
=30
100
50
0
(b)
100
150
200
250
300
Circle Projection Histogram
θ
=60
100
50
0
(c)
100
150
200
250
300
Circle Projection Histogram
θ
=90
100
50
0
(d)
100
150
200
250
300
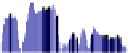
Fig. 2.
Circular region (or ROI) projection histogram. (a) Original images and the
projection histogram. (b) Rotated 30 degrees ROI and the projective histogram. (c)
Rotated 60 degrees ROI and the projection histogram. (d) Rotated 90 degrees ROI
and the projective histogram.
are projected into the 1D space. The computing complexity is greatly reduced.
The projection histograms at the same angle have rotation invariant features. 360
histograms can be obtained by projecting the ROI at the 360 directions.
Fig.2 shows an example for projection histogram with the ROI and its part of
rotated versions (
θ
=0
,
30
,
60
,
90). Finally, projection histograms of the template
ROI as the columns are grouped into a matrix, which is regarded as the sparse
dictionary
D
t
of the template.
D
t
can be written as follows,
⎡
⎣
⎤
⎦
R
0
R
0
···
R
359
0
R
1
R
1
···
R
359
1
D
t
=
(7)
.
.
.
.
.
.
R
0
N−
1
R
1
N−
1
···
R
359
N−
1
































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search