Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Where
m
=
i
N
+1
,...,j,...,j
+
N
S denotes the 2D sliding windows, and xmn denotes the gray sequence of image
pixels. So median filtering has its own filtering window as well, the window shape
and size of 2D median filtering have a great effect on the filtering result. The
common 2D median filtering windows are as follows
−
M,i
−
M
+1
,...,
1
,...,i
+
Mn
=
j
−
N,j
−
Tabl e 1.
The common window shapes of median filtering
Name
3
×
3
square
5
×
5
cross
7
×
7
cross
Window shape
Fig. 2.
The results de-noised by median filters of different windows(noise intensity:
0.15)
Fig. 2 shows us that median filtering can remove salt& pepper noise in the
infrared image, the bigger the median filtering window is, the clearer the de-
noising effect becomes. Choosing an appropriate filtering window can reserve
the useful detail information of image, on the premise that does not influence
the fault diagnosis. So median filtering is desirable to remove salt& pepper noise
without any details considered.
2.3 Frequency Domain Low-Pass Filtering
What stated above is spatial domain filtering, and frequency domain low-pass
filtering is another effective method which is based on the image smoothing in
frequency domain. Noises in the image are mostly in the high frequency part
of frequency domain, the low-pass filter can retain the low-frequency informa-
tion while filtering high-frequency noise. Supposing
F
(
u,v
) denotes the Fourier
transformation of the original image, and
G
(
u,v
) represents the image through
the low-pass filter, then the mathematical expression of low-pass filtering could
be defined as
G
(
u,v
)=
H
(
u,v
)
∗
F
(
u,v
)
(5)















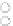




Search WWH ::

Custom Search