Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
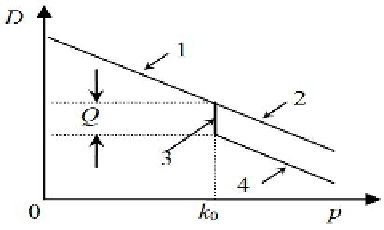
Fig. 1.
Demand curve with IL contract
0
<V <Q
. Therefore, the market demand for the wholesale market with the
IL contract can be illustrated by line segment 1, 3 and 4 in Fig. 1, and can be
formulated as follows:
⎧
⎨
A
−
bp,
if p < k
0
D
(
p
)=
(
A
−
V
)
−
bp, if p
=
k
0
(2)
⎩
(
A
−
Q
)
−
bp, if p > k
0
2.2 Cournot Equilibrium Model with IL Contract and Wind Power
Suppose that there are
n
conventional strategic generators and a certain number
of wind power units in the wholesale market with the IL contract, and the market
demand
D
is expressed as (2).
The conventional generator takes a form of quadratic cost function as follows:
C
i
(
q
i
)=0
.
5
c
i
q
i
+
a
i
q
i
,i
=1
,
2
,
···
,n
(3)
where,
q
i
is generator
i
s
output;
c
i
and
a
i
are cost parameters which are non-
negative.
Assume that the wind power units are price-takers in the market competition.
The output of wind power units in time
t
,
q
w
, is assumed to follow a normal
distribution with a mean value of
μ
and a standard deviation of
σ
.Themarket
demand
D
satisfies:
n
D
=
q
w
+
q
i
(4)
i
=1
Under the assumption of Cournot-type competition, the generators compete in
the wholesale market by bidding their power outputs. When the constraints on
generators' output and transmission capacity are ignored, generator
i
s
opti-
mization problem in the wholesale market can be described as:
Max
q
i
π
i
=
pq
i
−
C
i
(
q
i
)
n
(5)
s.t.q
i
=
D
(
p
)
−
q
w
−
q
j
j
=1
,j
=
i
Search WWH ::

Custom Search