Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
The PEM fuel cell model in this work is based on a 1.2 KW PEM fuel cell
power system, The structure of the PEM fuel cell system studied in this work
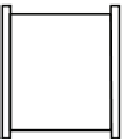
is shown in Figure 1.The supply of air/oxygen to the cathode is one of the key
factors in operation of the PEM fuel cell stack and it is also the subject in this
work.
Fig. 1.
The structures of a PEM fuel cell system
2.2 Oxygen Excess Ratio
The general proposed of this work is to design a control strategy to regulate the
oxygen excess ratio
λ
O
2
in the PEM fuel cell system. The oxygen excess ratio
has been defined in work [11] as
λ
O
2
=
w
O
2
,cain
/w
O
2
,react
.
(1)
where
w
O
2
,react
is oxygen consumption rate. It is proportional to the current
I
w
O
2
,react
=
nIM
O
2
/
(4
F
)
.
(2)
with
n
is the number of cells in the fuel cell stack, and
n
=46,
M
O
2
is the molar
mass of oxygen and
F
is the Faraday constant.
The oxygen flow rate
w
O
2
,cain
depends on the dry air flow rate
W
a,cain
:
w
O
2
,cain
=
μ
O
2
,cain
W
a,cain
.
(3)
μ
O
2
,cain
is the oxygen mass fraction, and it is equal to 0.233. And the mass flow
rate of dry air at the cathode inlet is described as
W
a,cain
=
W
cain
/
(1 +
ω
ca
)
.
(4)
ω
ca
=
M
v
P
v,cain
/
(
M
a,ca
P
a,cain
)
.
(5)
ω
ca
is the humidity ratio,
M
v
and
M
a,ca
are the molar mass of vapor and air at
the cathode inlet. The vapor pressure
P
v,cain
and the dry air pressure
P
a,cain
are defined as
P
v,cain
=
φ
ca,in
p
sat
|
T
.
(6)





















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search