Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Note that in the long chain each “SC” node must connect with at least ¸wo other
“SC” nodes, we have 2
m−
1
C
∗
.
In step 3, for given two short chains, if there are connected by link (
i
1
,j
2
)in
the minimum “spanning tree”, we find another link (
i
2
,j
1
) such that :
(
i
2
,j
1
)=arg
i,j
min
d
i
1
j
2
+
d
ij
−d
i
1
j
−d
ij
2
:
x
i
1
j
=
x
ij
2
=1
.
k
=1
D
k
≤
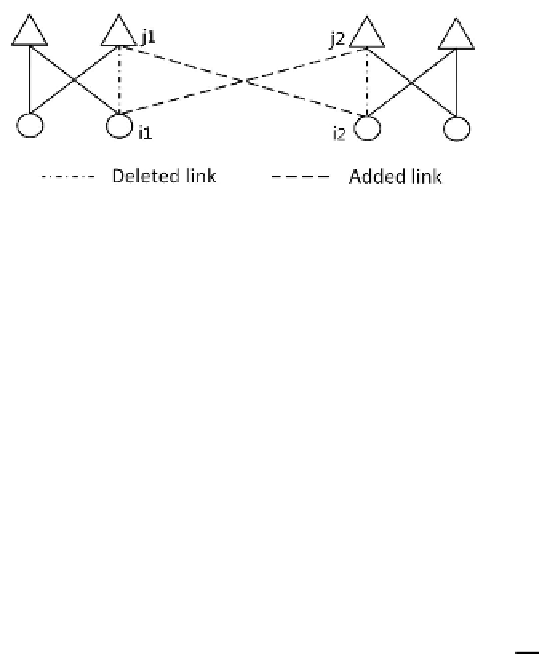
Then we merger these two short chains into one big chain by adding link (
i
2
,j
1
)
and deleting links (
i
1
,j
1
), (
i
2
,j
2
) as shown in Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.
Merger two short chains into one chain
Suppose that before merging these two short chains, the total cost is
C
,now
the total cost is given as
C
+
d
i
1
j
2
+
d
i
2
j
1
−
d
i
1
j
1
−
d
i
2
j
2
≤
C
+2
∗
d
i
1
j
2
, because
of the quadrangle inequality assumption, i.e.,
d
i
2
j
1
≤
d
i
1
j
2
+
d
i
1
j
1
+
d
i
2
j
2
.The
above analysis shows that the length of constructed long chain can be bounded
by
C
R
+2
m−
1
k
=1
D
k
C
∗
+
C
∗
=2
C
∗
. Thus, we give the following result.
≤
Proposition 2.
The proposed approximation algorithm is
2
-approximation al-
gorithm for the long chain design problem under QI assumption.
Proof.
In the above analysis, we have shown that the proposed algorithm pro-
vides solution at worst 2 bounded by time optimal solution.
Next we only need to construct an worst-case instance. Consider the instance
where all
m
“SC” nodes are evenly distributed on the circle with radius
R
=
m
.
Suppose each “SC” node contains two plants and two products, which are close
enough such that the total cost within each “SC” node is less than
m
2
. Figure
3. gives the “minimum spanning tree”. For large enough
m
, the objective value
obtained by the proposed algorithm can be estimated by
1)sin(
π
m
)+
m
1
1)sin(
π
m
)+
1
C
(
m
)=2(
m
−
m
2
=2(
m
−
m
.
On the other hand, for large enough
m
, the optimal long chain is obtained by
connecting all adjacent “SC” node, thus its objective value can be estimated by




Search WWH ::

Custom Search